There are several ways to install packages on any Linux distribution, one of which is using the default package installer of the respective distribution. Using Deb file For Debian-based Linux distributions like Kali Linux, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and Debian, apps can be installed via their deb files. Deb files are setup files that act as a container that holds all the necessary components for installing an application.
There are two major benefits of using the deb files for package installations one, it gives access to specific software versions. Second, it allows the installation of packages that are not available in the Ubuntu default package manager repository. This guide will explain all possible ways to install a deb file on Ubuntu.
5-Ways to Install Deb File on Ubuntu
Deb file primarily contains two types of data, one contains the control information and the other contains the installation files. However, using the deb files for package installation on Ubuntu or on any other Debian-based Linux distributions can increase package management complexity. To install a deb file on Ubuntu there are five ways and to demonstrate them I will use the newly released Ubuntu 24.04:
1: Using Ubuntu Default Package Installer
One of the most popular and commonly used methods to install any application on Ubuntu and other Debian-based Linux distributions is using the apt package manager. The apt app installer can not only be used to install the packages via its repository but can also be used for installation via deb files. To install a deb file via apt on Ubuntu, use the below syntax in case the directory is same as that of the deb file:
sudo apt install ./[deb-file-name]Here, for illustration, I have installed TeamViewer on Ubuntu via its deb file using the apt package manager:
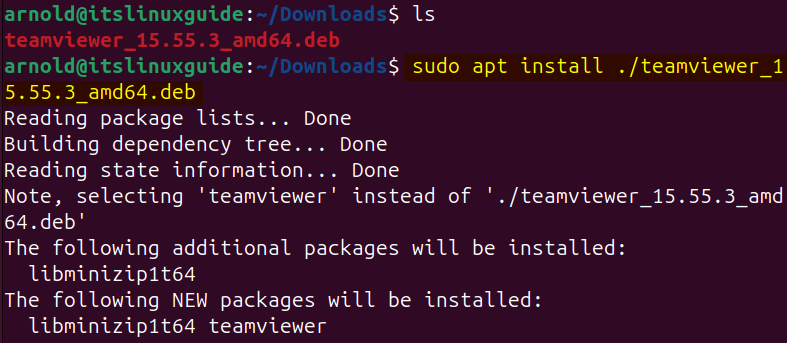
Next, if the deb file is in any other directory then instead of navigating to it, simply specify its path as in the syntax below:
sudo apt install [/deb-file-path/deb-file-name]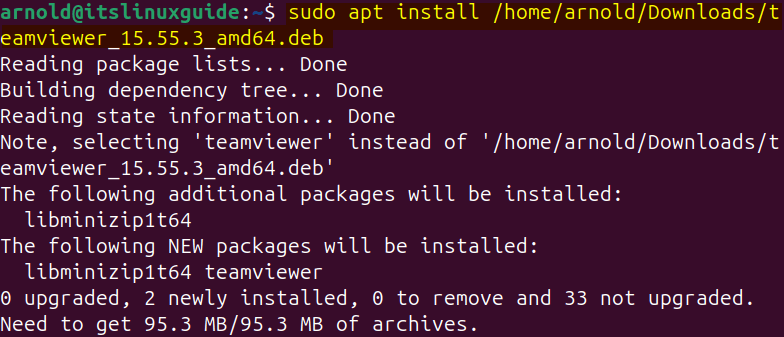
To look for the full path of the deb file, go to the respective file properties:
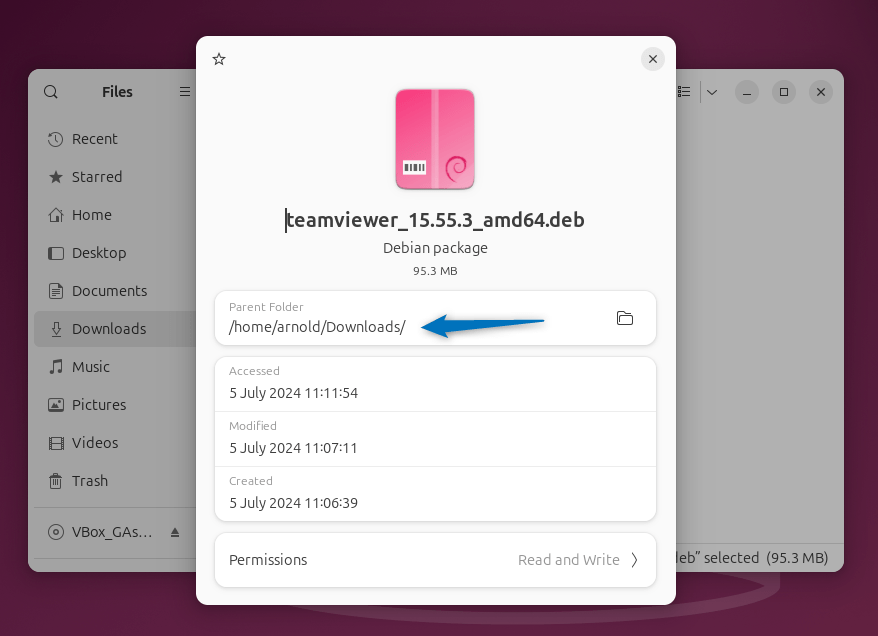
2: Using dpkg Package Manager
Another method to install deb files on Ubuntu is by using the Debian package manager (dpkg). It is a low-level package installer that only unpacks the deb file and then installs the package using its program files. One thing to remember is that dpkg unlike apt does not come with dependency management which can cause some dependency-related errors during the installation. To install a deb file via dpkg package manager on Ubuntu, use the below syntax:
sudo dpkg -i ./[deb-file-name]Here, for illustration, I have installed Google Chrome on Ubuntu via its deb file using the apt package manager:
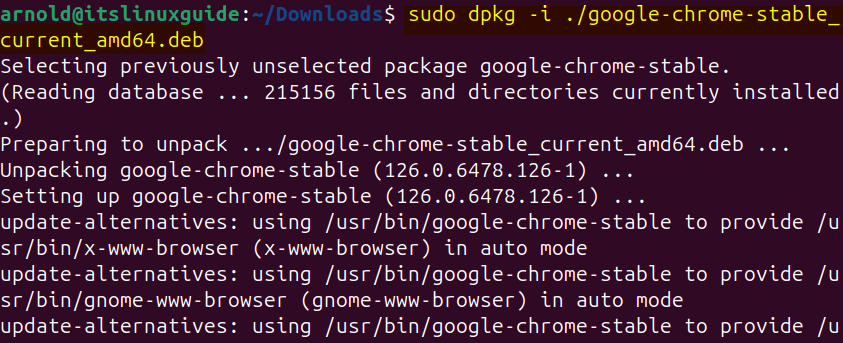
Next, if the deb file is in any other directory then instead of navigating to it, simply specify its path as in the syntax below:
sudo dpkg -i [/deb-file-path/deb-file-name]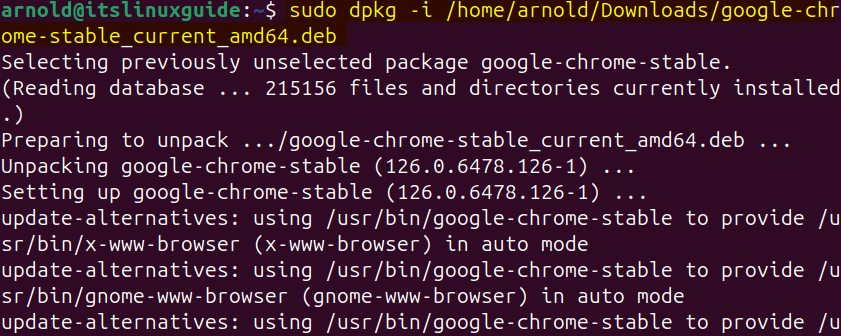
3: Using GDebi Package Installer CLI
The next method to install the Deb file on Ubuntu is by using the GDebi package installer which unlike dpkg can handle basic dependency resolution. It attempts to identify and install any essential dependencies required by the DEB package being installed. Further, a deb file can be installed either using the CLI or its GUI version. In the case of the GDebi CLI version, use the below syntax:
sudo gdebi ./ [deb-file-name]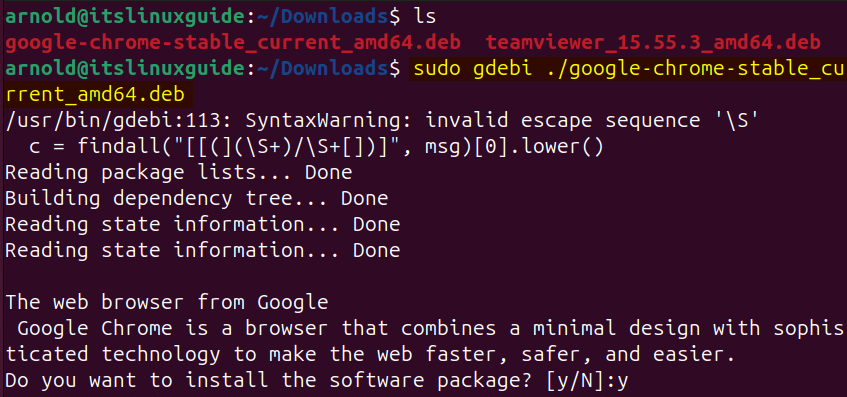
Next, if the deb file is in any other directory then instead of navigating to it, simply specify its path as in the syntax below:
sudo gdebi [/deb-file-path/deb-file-name]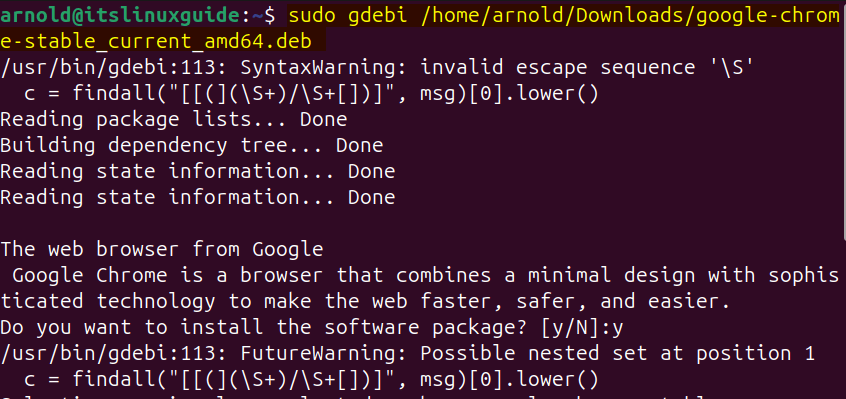
4: Using GDebi Package Installer GUI
The next method for installing the Deb packages on Ubuntu is to use the GUI version of the GDebi package installer. To launch it, either use the apps menu or run the below command in the terminal:
gdebi-gtk
To install deb files you need to open them in the GDebi package installer by clicking on the Open option in the File menu:
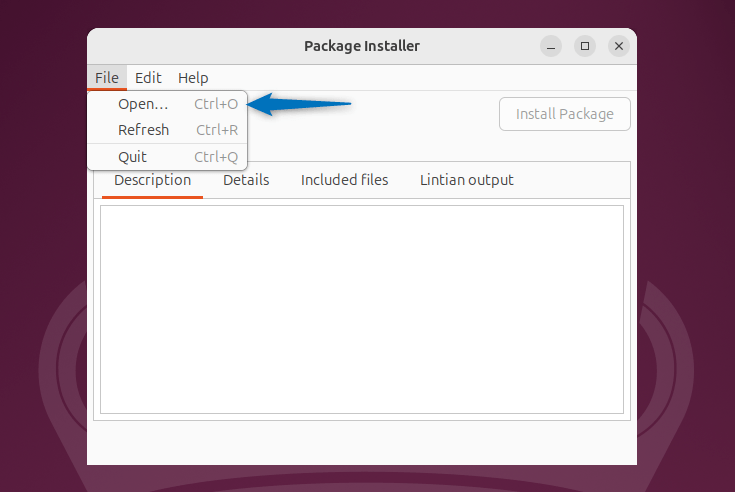
Now navigate to the location where the deb file is placed, then select the deb file and click on Open:
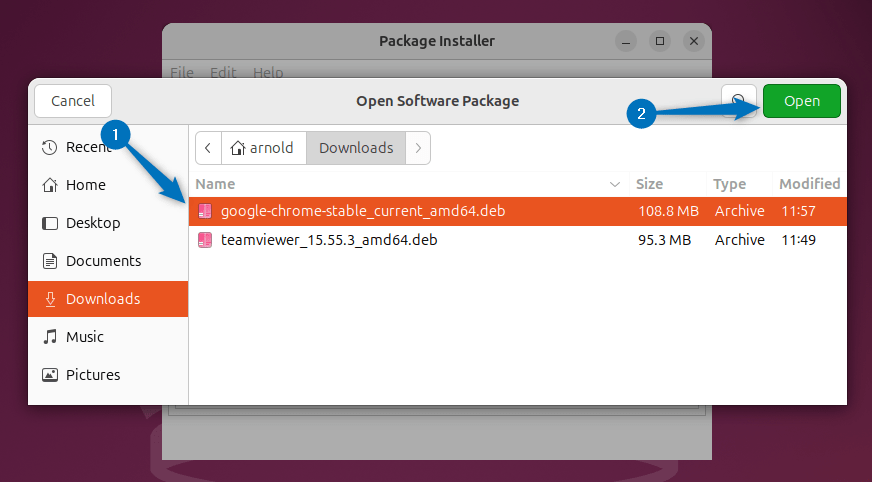
Once the Deb file is loaded in GDebi click on the Install Package option to proceed with installation:
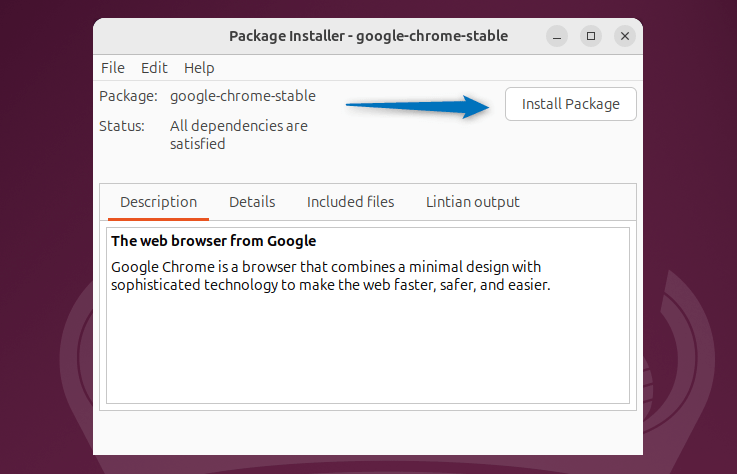
Once the installation is finished, close the dialogue box and launch the installed application:
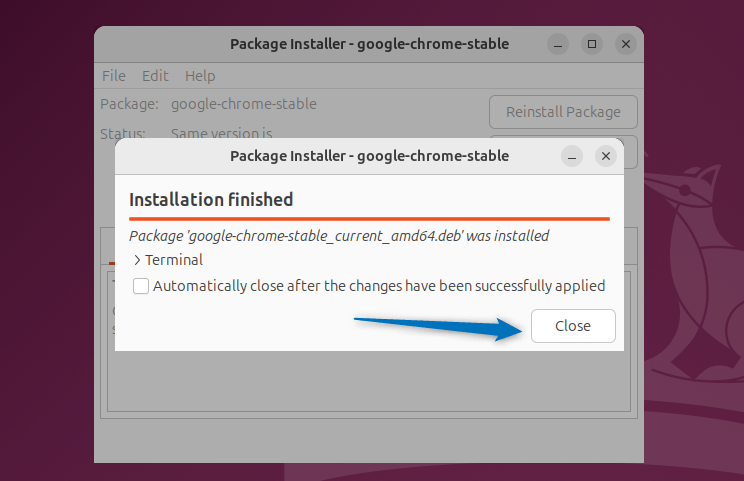
Note: GDebi package installer by default is not installed on Ubuntu, so to install it use the App Center:
5: Using Ubuntu Software App
The last and fifth method to install a deb file on Ubuntu is by using its Software app, first open the Deb file with the Software Install option:
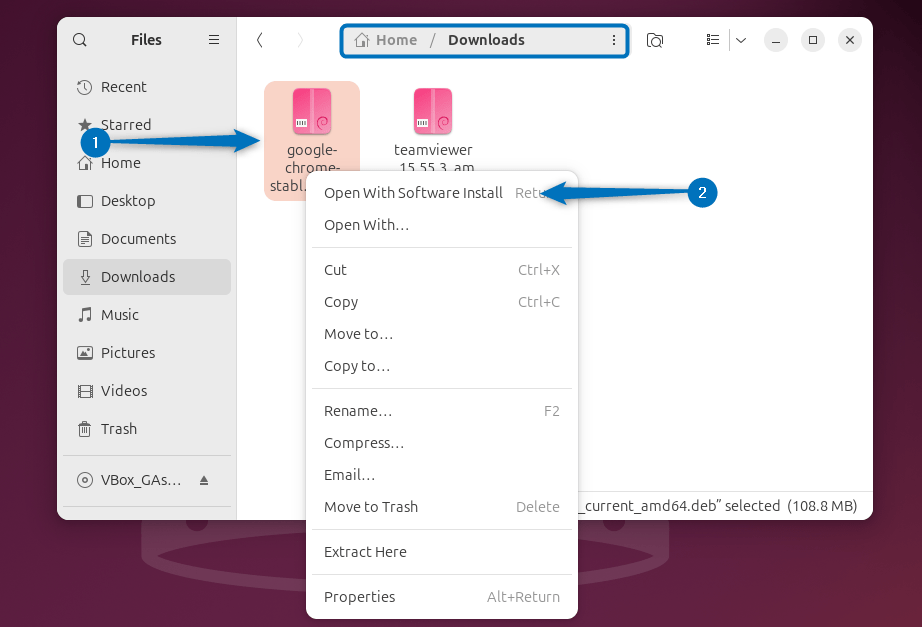
Next, once the Deb file is loaded, click on the Install option to proceed with the installation:
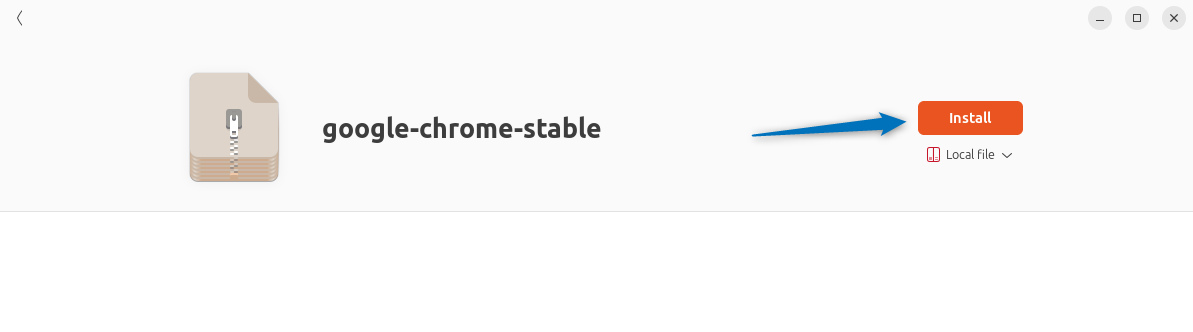
Once the installation is finished you will see the icon image of that respective application appear, you can either launch the app by clicking on the Open button or through the app menu:

How to Fix Unable to Locate Software Install on Ubuntu
Sometimes while installing Ubuntu, the Software Install option in the Open With menu may not be unavailable. This is because by default, the GNOME software package is not installed, which includes this Software Install app. So run the below command to install the Gnome-software package via apt:
sudo apt install gnome-software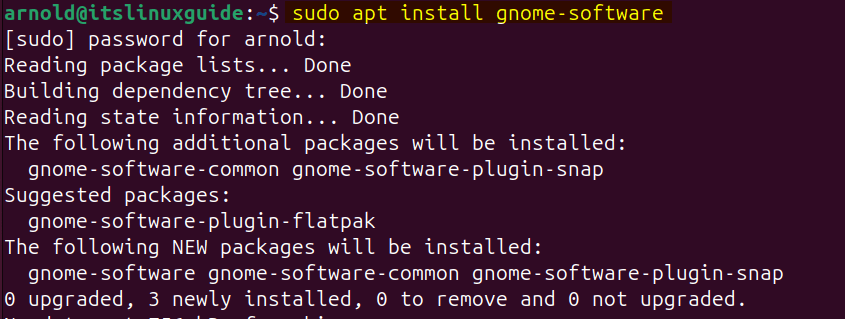
Difference Between apt, dpkg, GDebi and Ubuntu Software
To further clarify the difference between all these methods discussed above for the installation of deb files on Ubuntu, here are some of the key differences in the below table:
| Differences | Apt Package Installer | Dpkg Package Installer | GDebi Package Installer | Ubuntu Software (GNOME-Software) |
| Functionality | Install, remove, update, and manage packages | Install, remove, and query packages | Install, and remove packages (basic dependency handling) | Install, remove, update, and manage packages |
| Dependency Management | Robust | No automatic dependency management | Basic dependency handling | Robust |
| Use Case | Mostly used for package management | Advanced users, troubleshooting specific package issues | Beginners, installing local DEB files | Mostly used for package management (GNOME desktop) |
| Interface | Command-line | Command-line | Command-line and Graphical | Graphical |
Conclusion
To install a deb file on Ubuntu there are five different ways that this guide discussed, these include using apt package manager, dpkg package manager, both GDebi CLI and GUI versions, and the Ubuntu software app. If you are looking for an easy CLI method then use the apt package manager and if you are looking for a GUI method then use the Ubuntu Software Install app.
