Virtualization is primarily used to create virtual versions of computer resources, such as servers, storage, networks, and even desktops. Virtualization allows quicker application deployment and easier scaling of resources when needed. VirtualBox is one of the popular virtualization platforms that allows you to create virtual machines (VMs) that can run various operating systems. Ubuntu because of its wide community support and user-friendliness is the most preferred Linux distribution. If you want to create a virtual machine on Ubuntu using the VirtualBox, then read this guide.
4 Ways To Install VirtualBox on Ubuntu
VirtualBox is an open-source and free-to-use virtualization platform that comes with a wide range of support for operating systems. Further, it is the best option as compared to VMware in case you are planning to use it for personal purposes or light commercial use. There are primarily four main ways to install VirtualBox on Ubuntu which this guide will explain:
1: Using VirtualBox Deb file
The first method to get VirtualBox on Ubuntu is using its Deb file, which you can download from VirtualBox official site. Here I have selected the latest version of VirtualBox which is compatible with the Newly released Ubuntu 24.04:
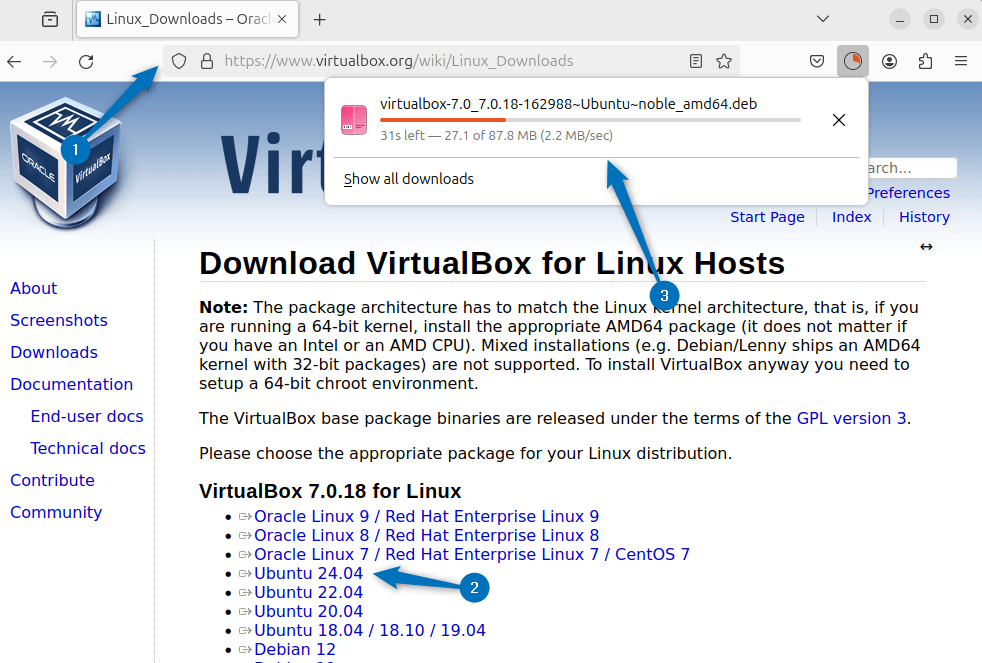
Now there are three ways to install deb files on Ubuntu (apt,dpkg and gdebi), here I have used the apt package manager for VirtualBox installation:
sudo apt install ./virtualbox-7.0_7.0.18-162988~Ubuntu~noble_amd64.deb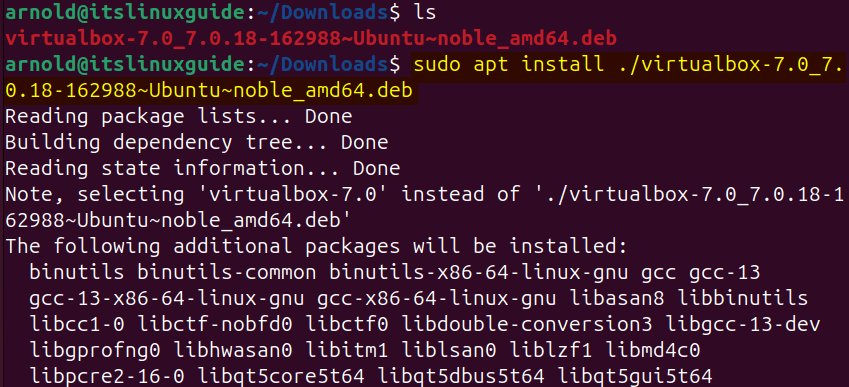
Now launch the VirtualBox using the terminal once the installation is successfully completed :
virtualbox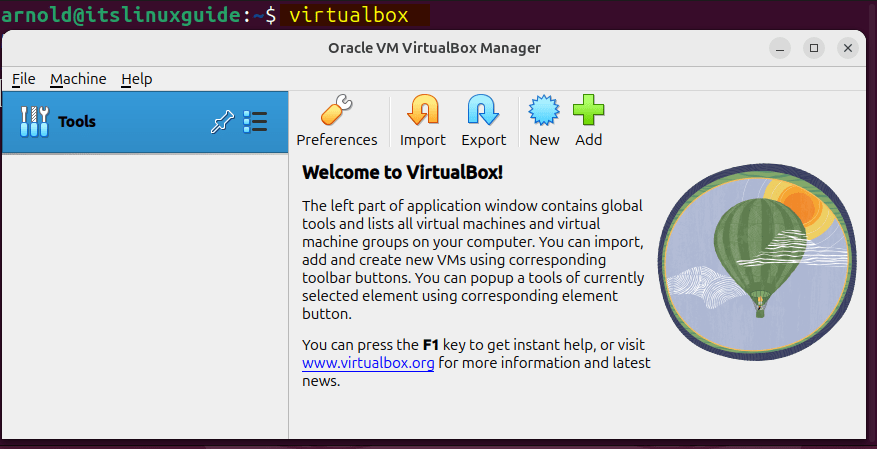
2: Using the Ubuntu Default Package Manager
Another method to install VirtualBox on Ubuntu is using its default package installer, however apt contains the older version of VirtualBox. If you are fine with using the older version then use this method as it is the easy one:
sudo apt install virtualbox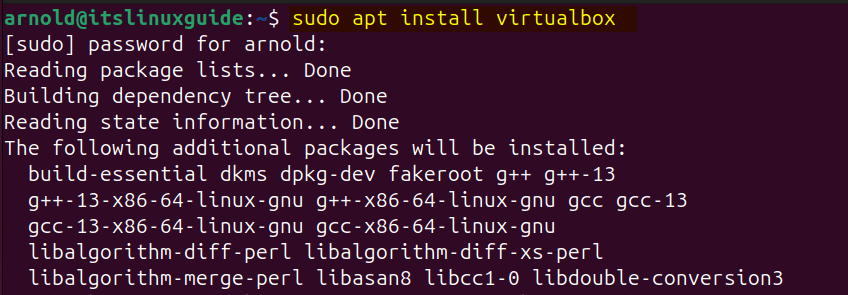
To verify the VirtualBox installation, I have used its help option to check the version:
VirtualBoxVM --help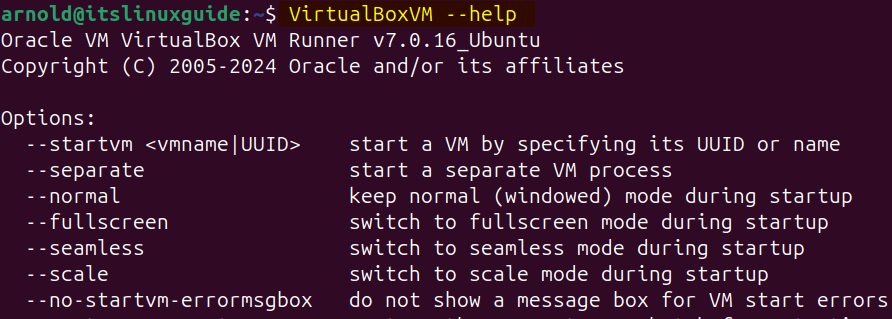
3: Through VirtualBox Repository
The third method to install VirtualBox on Ubuntu is using the VirtualBox repository, however there is a chance that this repository might get deprecated at any time. Adding the repository is beneficial when either there is no other way to install a package or the default package manager doesn’t have the respective package. To validate the repository on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions it is necessary to add their GPG key:
curl -fsSL https://www.virtualbox.org/download/oracle_vbox_2016.asc|sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/vbox.gpg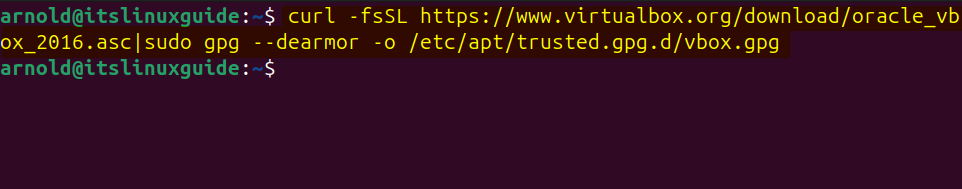
Now add the VirtualBox repository in the sources directory using the echo command:
echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian $(lsb_release -cs) contrib" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/virtualbox.list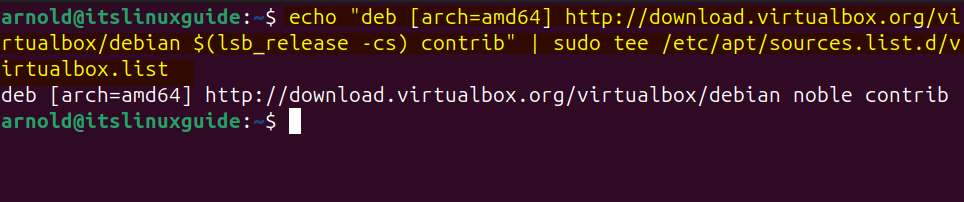
After adding a repository in the default package installer it is necessary to update its packages list, in case of Ubuntu execute:
sudo apt update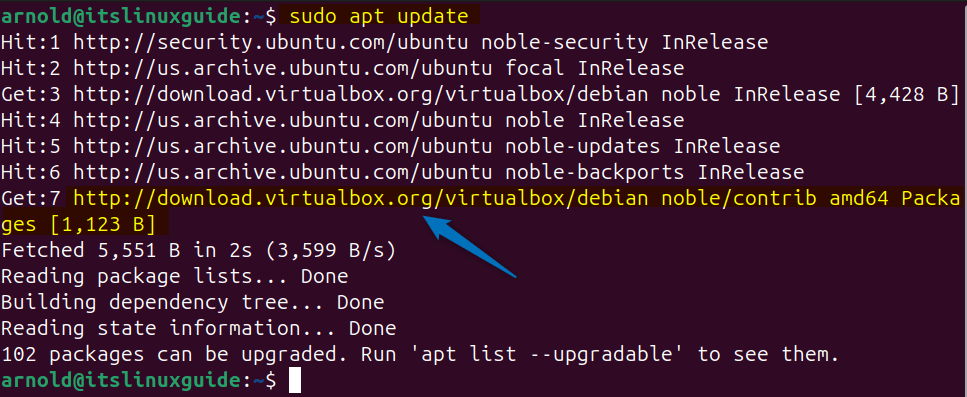
Now install VirtualBox on Ubuntu using its repository:
sudo apt install virtualbox-7.0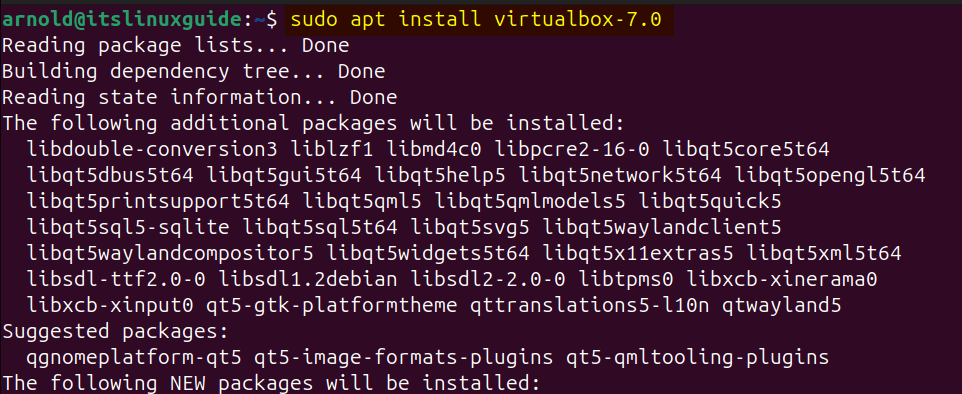
To verify the VirtualBox installation, I have used its help option to check the version:
VirtualBoxVM --help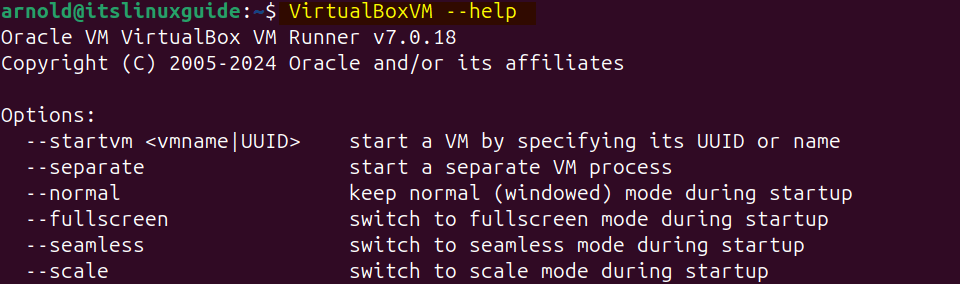
Further, to launch VirtualBox on either use the virtualbox command or use its applications menu:

4: Through the Gdebi Package Manager
There are several ways to install an application via its Deb file, one of which is Gdebi package manager. In the case of VirtualBox, you first need to install Gdebi by executing:
sudo apt-get install gdebi-core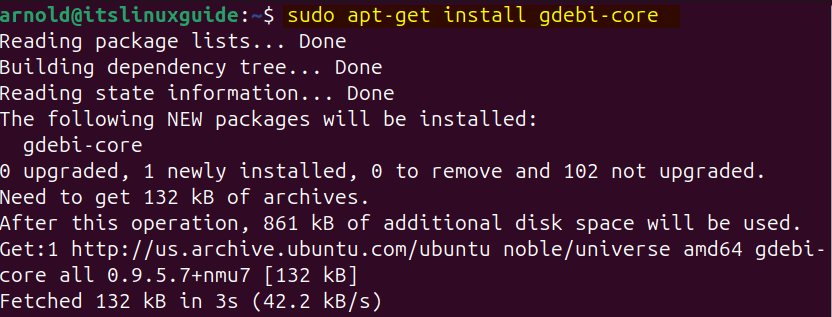
Next, use the VirtualBox Deb file to install it via Gdebi package manager:
sudo gdebi virtualbox-7.0_7.0.18-162988~Ubuntu~noble_amd64.deb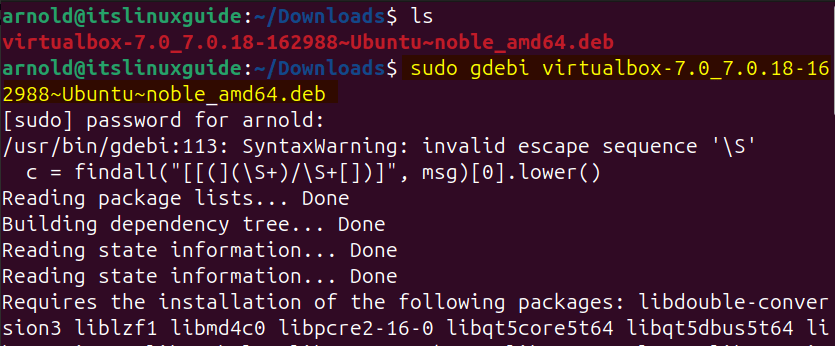
How to Install VirtualBox Extension Pack on Ubuntu
In case you encounter any problems while creating a virtual machine, or you need some additional features and add-ons, then install its extension pack. The patch for VirtualBox 7.0.18 is supported for all types of platforms, download the extension pack from the VirtualBox download page:
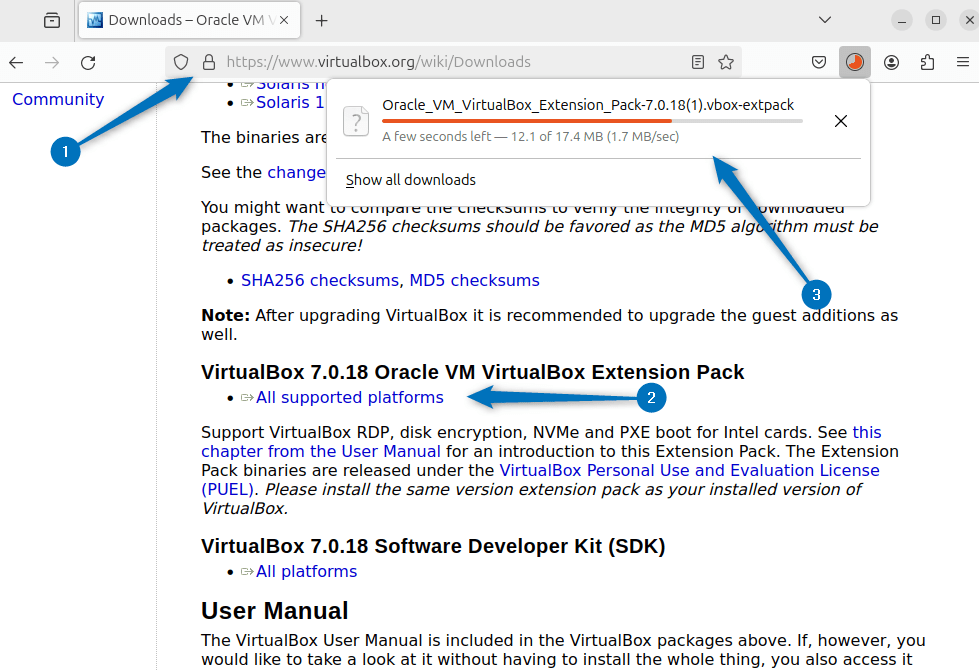
Next, open the extension pack location and open it with VirtualBox:
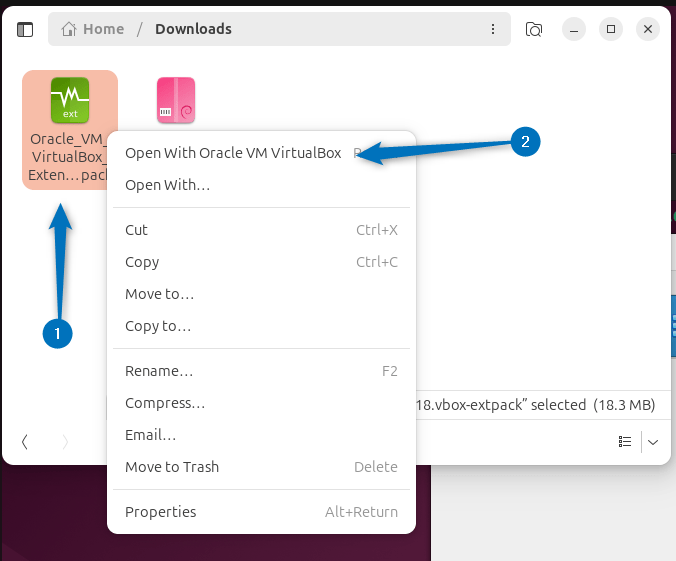
Now click on the install option to proceed with installation:
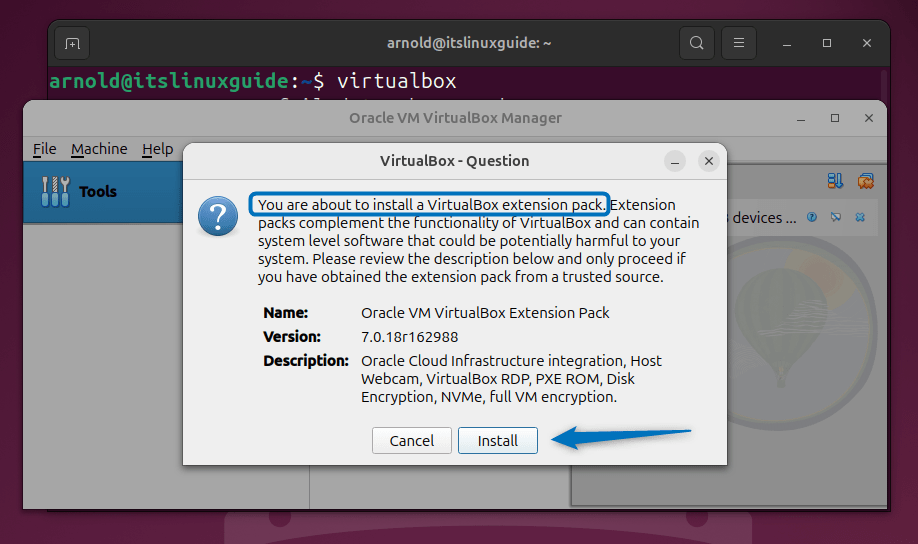
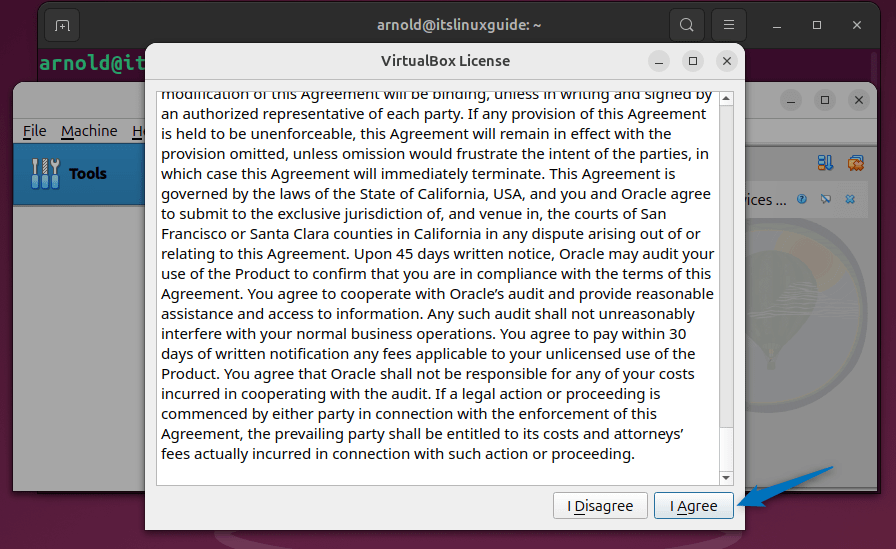
To prompt the installation, agree to the terms and conditions of the VirtualBox license and next the patch will be installed:
Conclusion
VirtualBox on Ubuntu can be installed in four different ways, which include using its Deb file, VirtualBox repository, Gdebi package manager, and apt package manager. To enjoy the seamless VirtualBox experience, the best installation method is using its deb file. Further, if you need some extra functionalities of VirtualBox then you can install its extension pack.
