Terraform is a critical tool for DevOps workflows, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud-native architectures, aiming to achieve scalability and automation in infrastructure management. For Ubuntu and other Linux systems, it integrates seamlessly and aligns with the way Linux administrators and DevOps typically manage infrastructure. This guide will discuss several ways to install Terraform on Ubuntu.
4 Ways to Install Terraform on Ubuntu
Terraform comes with a resource graph that provisions them in the correct order and in parallel where possible, optimizing deployment speed. There are four ways to install it on Ubuntu that this guide will explain:
1: Through Terraform Repository
Terraform by default is not available in the apt repository, so one way to install it on Ubuntu is by adding its repository manually. First, download its GPG key for validating the repository by executing:
wget -O- https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg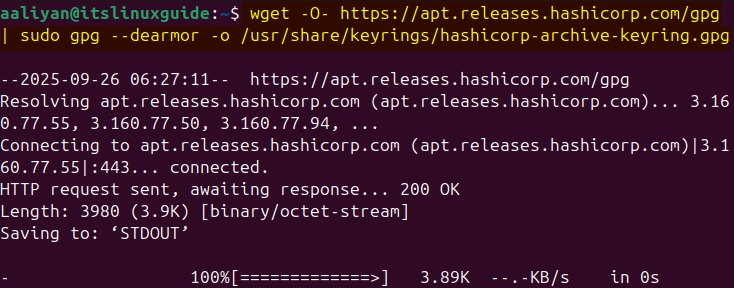
Now download its repository signed via the GPG key downloaded previously:
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/hashicorp-archive-keyring.gpg] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(grep -oP '(?<=UBUNTU_CODENAME=).*' /etc/os-release || lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hashicorp.list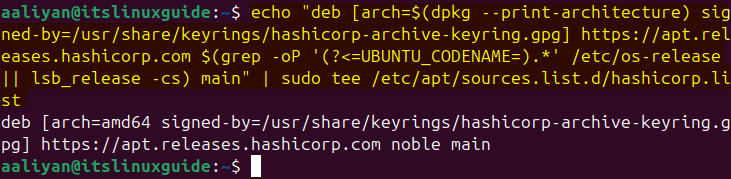
Next, to successfully integrate its repository, update the apt repository by executing the command below:
sudo apt update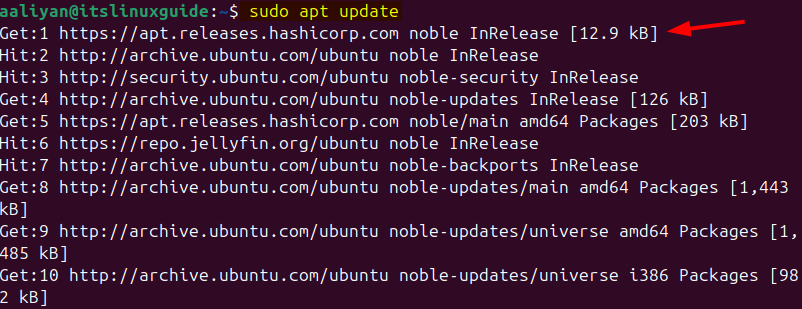
Now install it on Ubuntu via the apt package installer by executing:
sudo apt install terraform -y
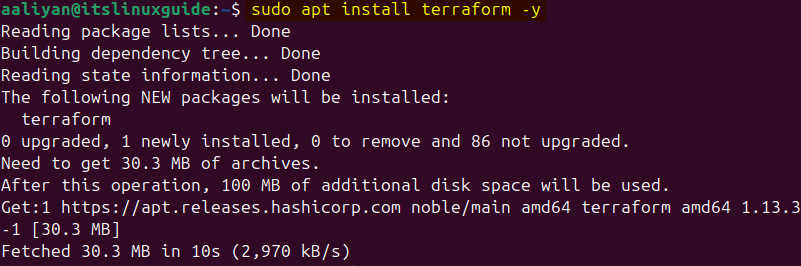
To verify the installation, check its version using the command below:
terraform --version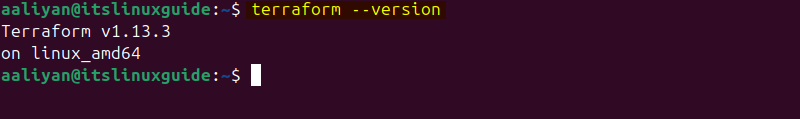
2: Through the Terraform Source File
Terraform also comes with its plug-and-play version, as it does not require any installation. Download the Terraform zip file from its official download page after selecting the OS:
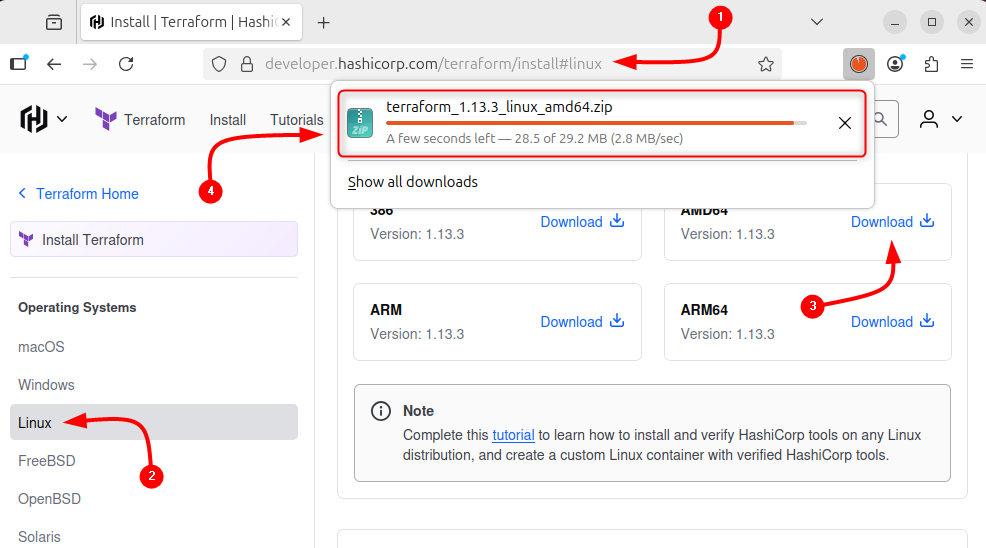
Alternatively, its zip file can be downloaded via the terminal by using the download link as in the command below:
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.13.3/terraform_1.13.3_linux_amd64.zip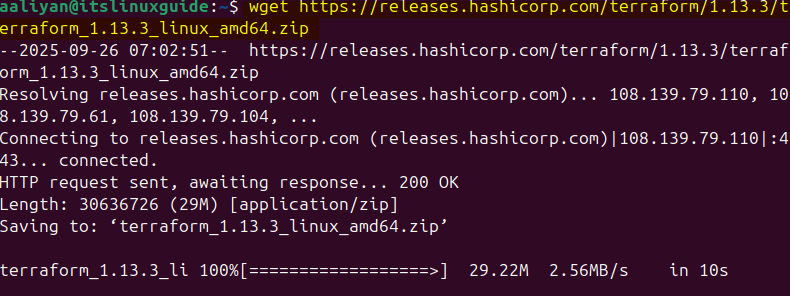
Now use the unzip utility to extract its zip file by executing the following command:
sudo unzip terraform_1.13.3_linux_amd64.zip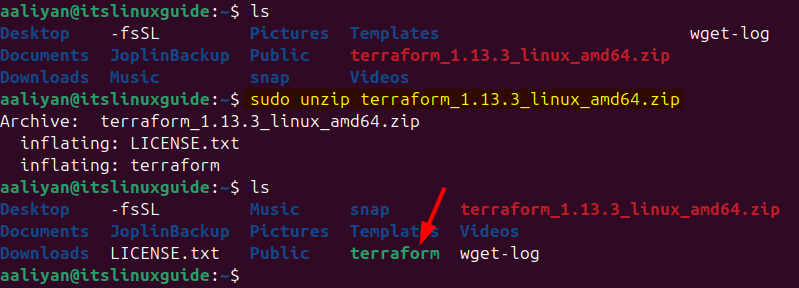
The extracted folder is itself an executable, so simply check its version by using the version command as given below:
./terraform --version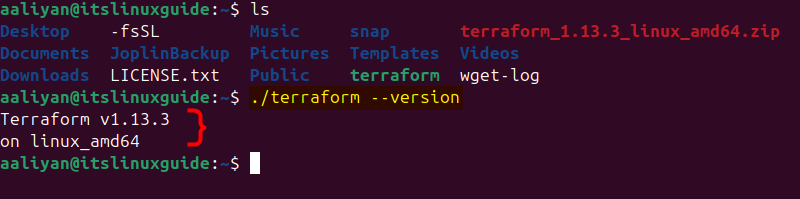
Furthermore, to access it from anywhere in the system, move the folder to the bin directory of Ubuntu using the mv command:
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/ -v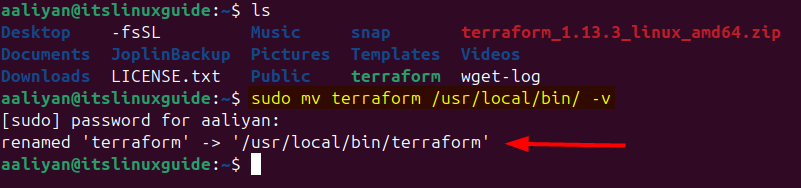
3: Through the Snap package Installer
Terraform can also be installed via the snap package installer; however, it contains an older version as compared to the previous methods. To install it via snap, execute:
sudo snap install terraform --classic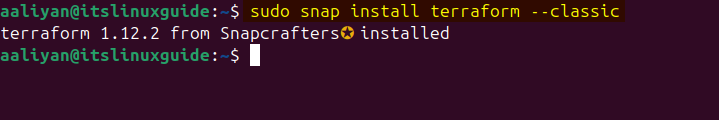
Once the installation is completed, first check the path where it is installed on Ubuntu, and then check its version for verification. Usually, packages installed via snap are in its bin directory:
which terraform
./terraform --version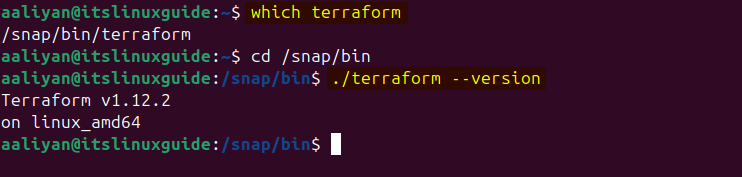
4: Through Ubuntu App Center
Terraform, though it is a command-line tool, but still it can be installed via Ubuntu App Center, which, in other words, is a GUI version of Snap Store:
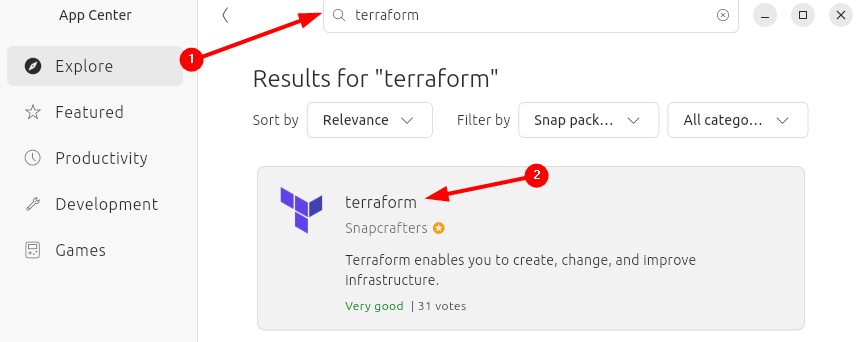
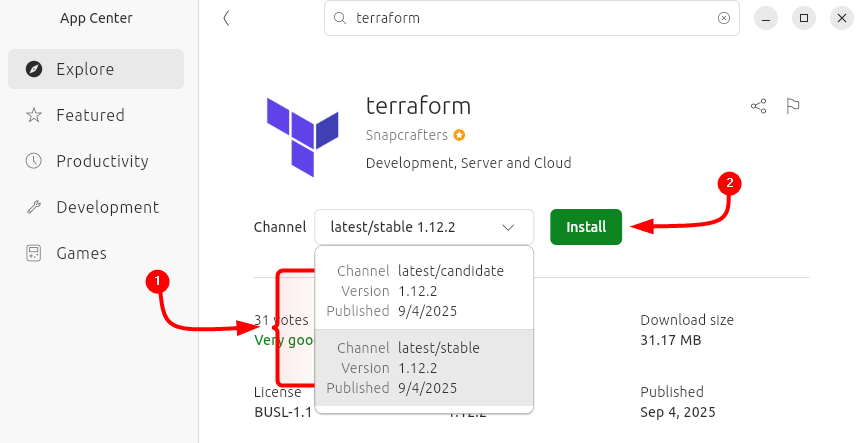
After searching for Terraform, select its channel, as there are two types of channels: one is a candidate that is a pre-release channel that has builds that the publisher thinks are almost ready for stable, but still need a bit of testing. I have selected the second channel, which is the main stable release track:
Since it is also via Snap Store so it is installed in the snap bin directory:
which terraform
./terraform --version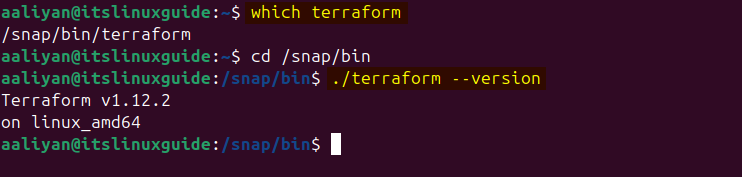
Conclusion
Terraform is a code infrastructure tool that removes the manual steps in infrastructure management, ensuring infrastructure is consistent and repeatable. This guide discussed four ways to install Terraform on Ubuntu, which include using its repository, source file, snap store, and Ubuntu App Center.
