MongoDB is a database built for modern applications that require flexibility, scalability, and performance, making it a popular choice among developers building dynamic, data-driven systems. Debian-based Linux systems seamlessly integrate with MongoDB through native .deb packaging, systemd, and service management. This guide will discuss 3 ways to install MongoDB on Debian, along with some of its configuration steps.
3 Ways to Install MongoDB on Debian
MongoDB does not require predefined schemas, so fields can be added or modified at any time without re-structuring the entire database. There are 3 ways to install MongoDB on Debian, which this guide will discuss, along with 4 steps for getting started with MongoDB:
1: Through the MongoDB Repository
The apt package installer does not come with the MongoDB package, so one way to install it on Debian is by manually adding its repository. First, download its public GPG key to verify it with the MongoDB database, and then register MongoDB’s signing key with the system’s package manager:
curl -fsSL https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-7.0.asc | \
sudo gpg -o /usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg \
--dearmor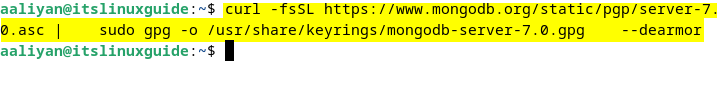
Next, add the MongoDB repository to the apt package installer by executing:
echo "deb [ signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg ] http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian bookworm/mongodb-org/7.0 main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-7.0.list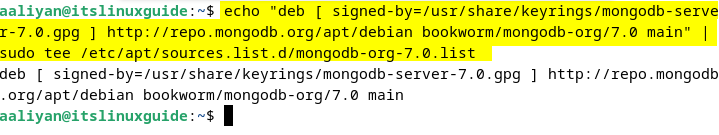
Now update the apt repository list to integrate the MongoDB repository by executing:
sudo apt-get update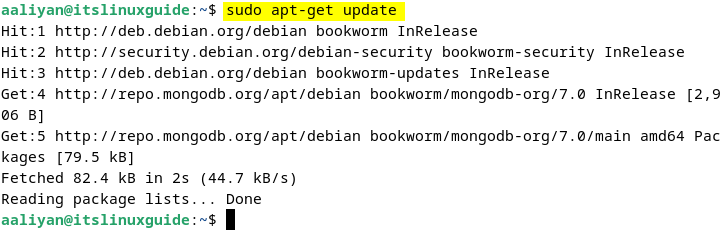
Now install MongoDB on Debian via apt, which installs mongos and mongod, which are the packages for the Mongo sharding router and MongoDB server daemon:
sudo apt-get install mongodb-org -y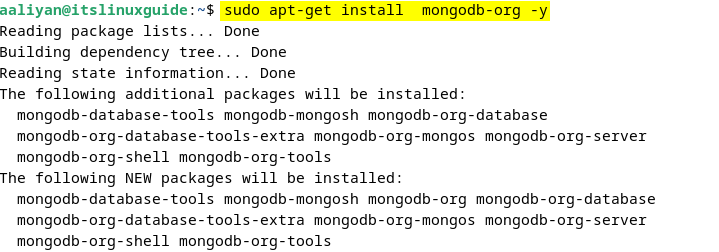
To verify the installation of MongoDB, check its version by executing:
mongod --version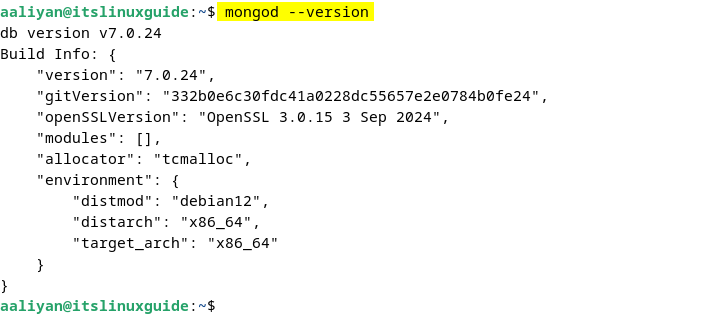
2: Through the MongoDB .deb File
Installing applications via .deb files on Debian-based Linux systems offers several advantages, one of which is that it automatically ensures all required dependencies are installed. To download MongoDB .deb, visit its official download page:
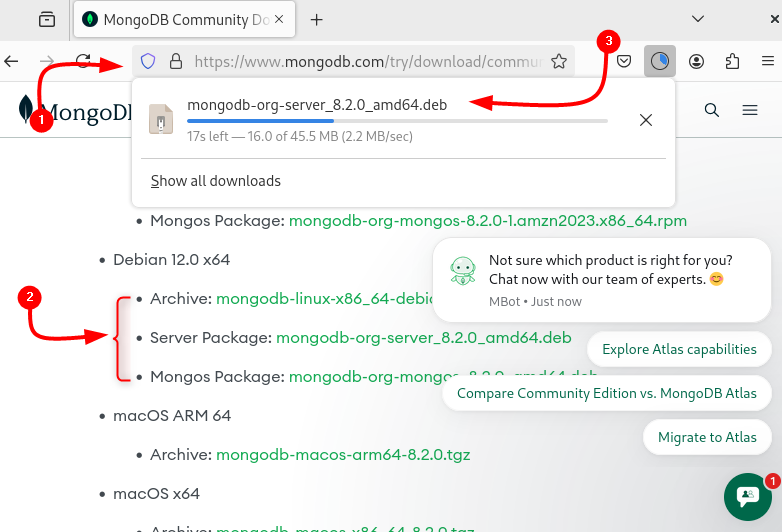
As in the image above, there are two .deb files, one is the Mongos Package and the other is the Server Package. The server package is a standalone MongoDB server (no sharding, no extra tools), whereas the Mongos package installs a sharded MongoDB cluster. Here, I have downloaded the Mongo server package:
wget https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian/dists/bookworm/mongodb-org/8.2/main/binary-amd64/mongodb-org-server_8.2.0_amd64.deb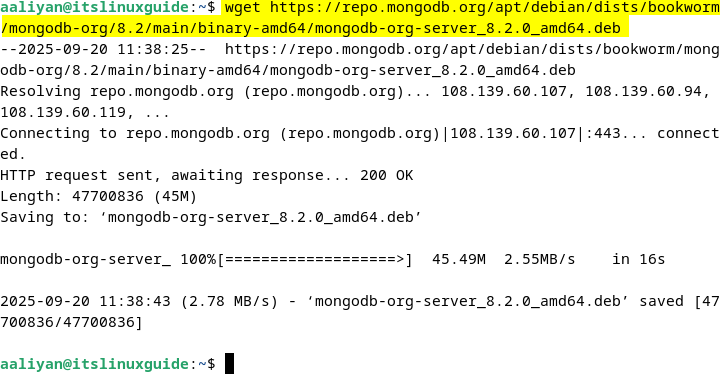
Next, using the Debian default package manager to install the MongoDB server package by executing:
sudo apt install ./mongodb-org-server_8.2.0_amd64.deb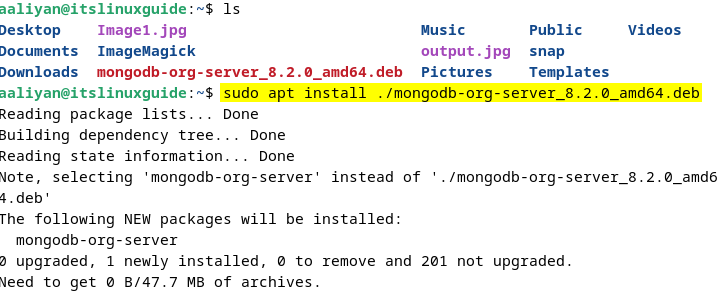
The .deb file comes with a comparatively newer version of MongoDB, which is 8.2.0, and to check the version, execute:
mongod --version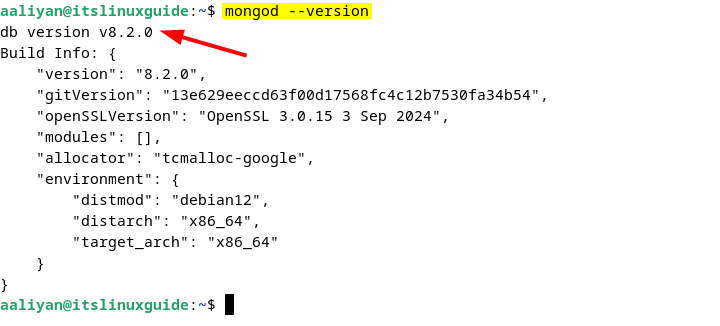
3: Installing MongoDB Compass (GUI)
The MongoDB Compass is not the entire package for MongoDB, but it is a GUI that provides visual interaction with MongoDB databases. Several administrative tasks, such as enabling/disabling authentication, managing replica sets, Sharding administration, and Backup/restore, can only be performed via the CLI. To install MongoDB Compass, download its .deb by executing:
wget https://downloads.mongodb.com/compass/mongodb-compass_1.46.10_amd64.deb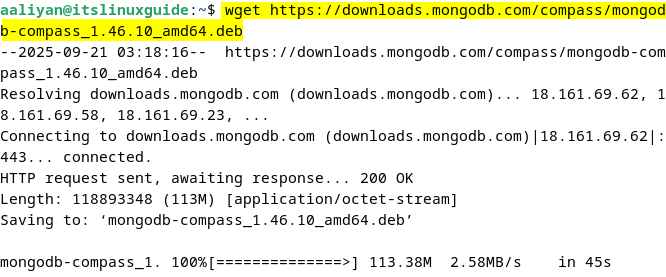
Next, use the apt package manager to install Compass using its .deb file :
sudo apt install ./mongodb-compass_1.46.10_amd64.deb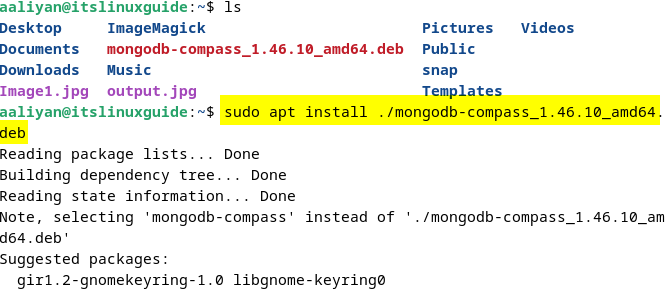
MongoDB Compass can be launched via both the App menu and via CLI by executing:
mongodb-compass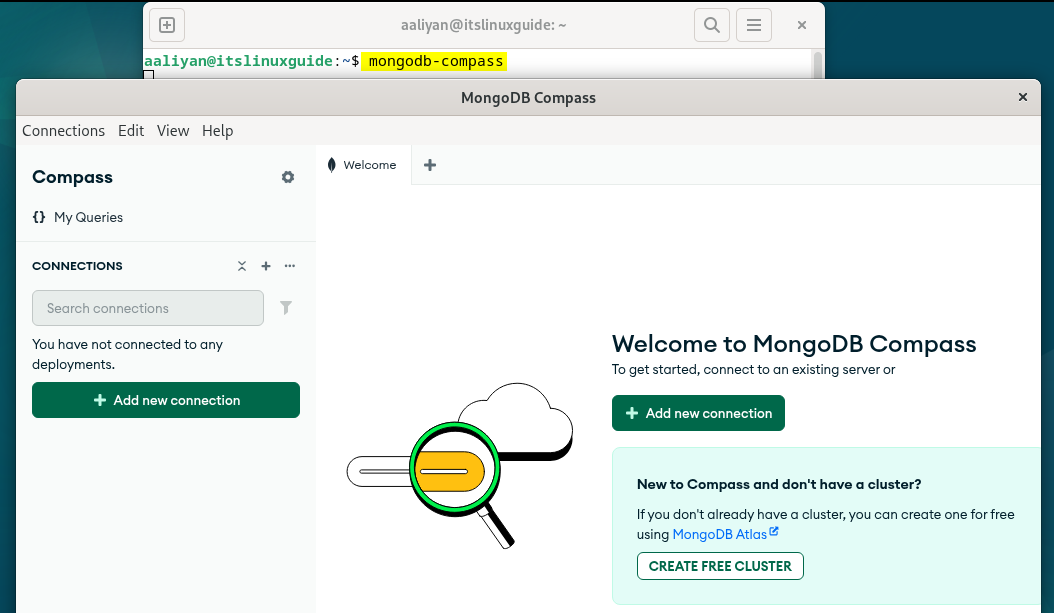
Note: To use MongoDB properly, it is necessary to install its shell as well, and for that, first download its GPG key by executing:
wget -qO- https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-8.0.asc | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/server-8.0.ascNext, add the mongosh repository in the apt installer by executing:
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian bookworm/mongodb-org/8.0 main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-8.0.listAfter updating the apt repository list, install mongosh by using the command below:
sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-mongoshSteps to Configure MongoDB on Debian
Getting started with MongoDB requires some necessary configuration steps, like starting the service, editing the configuration file, and connecting the database with MongoDB Compass
Step 1: Enable the MongoDB Service
By default, the MongoDB service is inactive and disabled after its installation, so to check its status, execute the following command:
sudo systemctl status mongod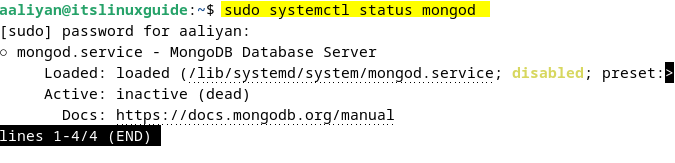
To activate and enable the MongoDB service on Debian, use the systemctl utility as in the commands below:
sudo systemctl start mongod
sudo systemctl enable mongod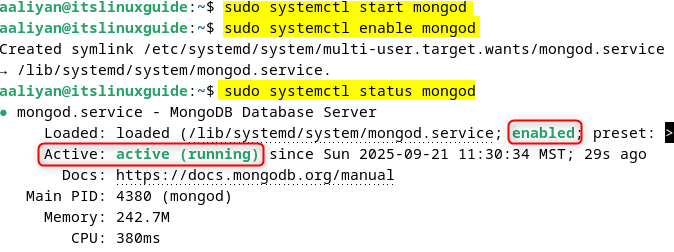
Step 2: Enable Authentication
To make any changes to the MongoDB configuration, edit the mongod.conf file. To secure the database, enable the authentication feature, and for that, open the configuration file using :
sudo nano mongod.conf
Next, add the following code lines in mongod.conf under the security comment:
security:
authorization: enabled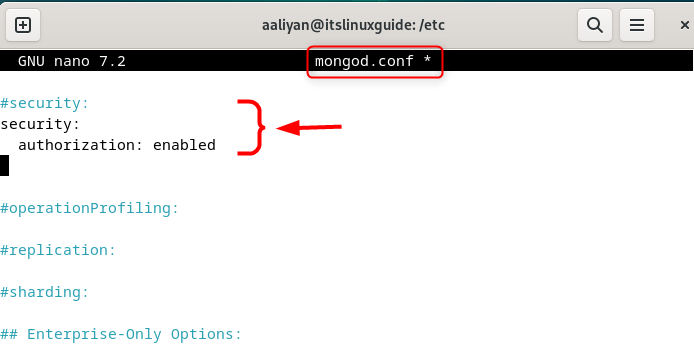
To apply the changes, restart the MongoDB service using the systemctl utility
Step 3: Create Database User and Password
The next step is to create a username and password for the database, and for that, launch MongoDB in the terminal and move to the admin:
mongosh
use admin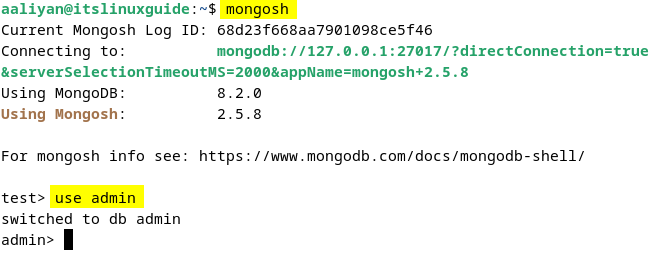
Next, use the following lines of code to create a username and prompt for setting the password:
db.createUser(
{
user: "itslinuxguide",
pwd: passwordPrompt(),
roles: [
{ role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" },
{ role: "readWriteAnyDatabase", db: "admin" }
]
}
)
Step 4: Connect with MongoDB Compass
Lastly, launch MongoDB Compass and click on the Add new connection to add the MongoDB database:
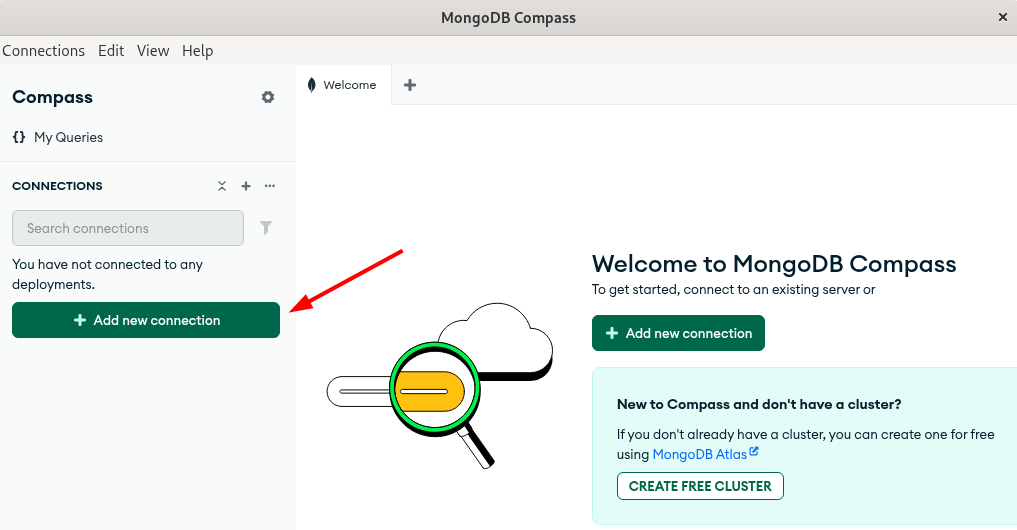
Here, add the connection URL, which includes the system IP address and port 27017:
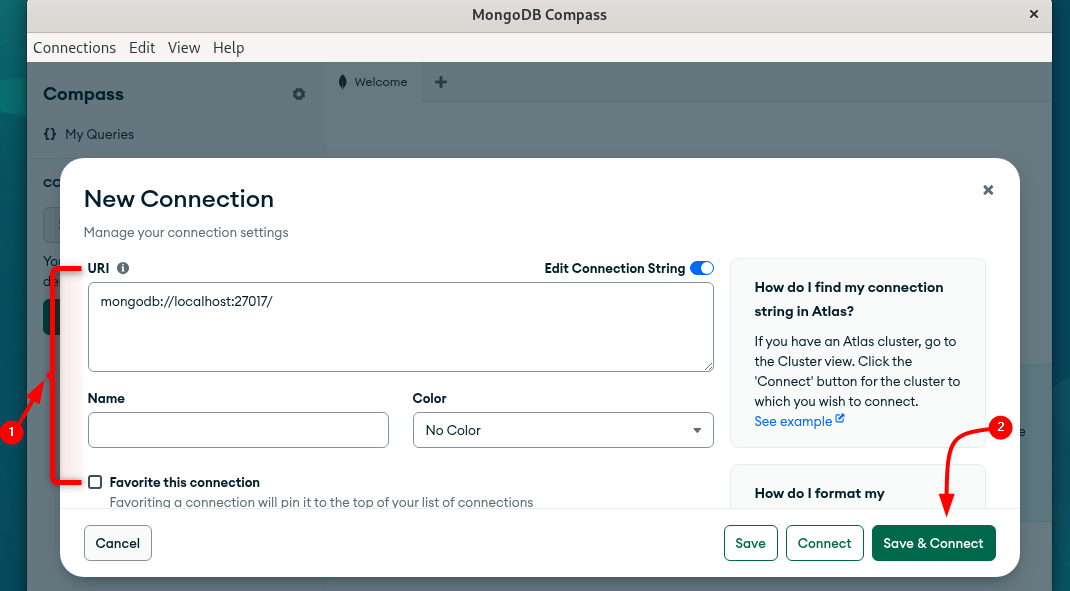
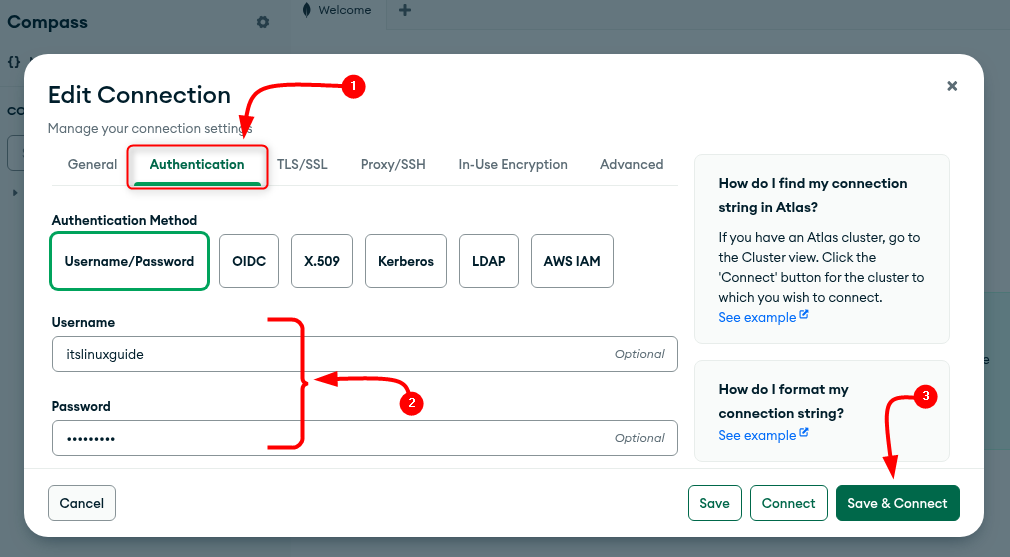
Since authentication is enabled, go to the advanced options by scrolling down, and from there go to the authentication tab. Here, enter the username and password created in the previous step, and afterwards click on Save & Connect:
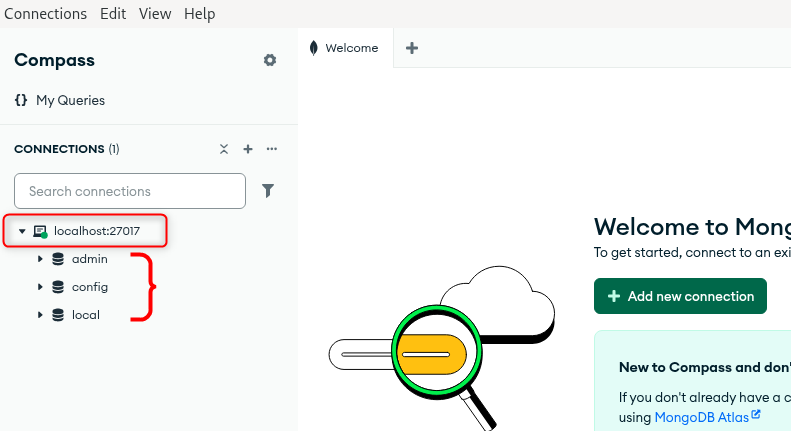
Now, once the database is connected, its directories will appear on the left side:
Conclusion
MongoDB is a database system that provides document-oriented storage, making the data model far more expressive and adaptable compared to rigid relational schemas. This guide discussed 3 ways to install MongoDB on Debian, which include using the MongoDB repository and. .deb file.
