Granting permissions to users for accessing Linux systems like Debian must be done with care, as giving unnecessary permissions can compromise the system’s security. On Debian and other Linux systems, users can be segregated into different groups. The group with administrator rights is named the sudo group in most Linux distributions, and to grant administrative permissions, it is required to add user to sudoers file in Debian. The users in this group are allowed to execute every type of command as they have full access to it.
6 Ways To Add User To Sudoers in Debian
The sudoers file is the configuration file for users with admin rights. It controls the behavior of the sudo command, which allows authorized users to run commands with administrative privileges. On Debian, when you create a new user and execute any command using sudo, you will probably get an error: the username is not in the sudoers file:

To grant a user admin rights or to add user to sudoers in Debian, this guide explains four methods. To follow any of the methods mentioned below, other than the GUI, log in to the administrative account via the terminal:
su -
1: Manually Assigning Permissions in Debian
The first method to add user to sudoers in Debian is by manually opening the sudoers file in the editor and adding the permission for execution of all types of commands:
[user-name] ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL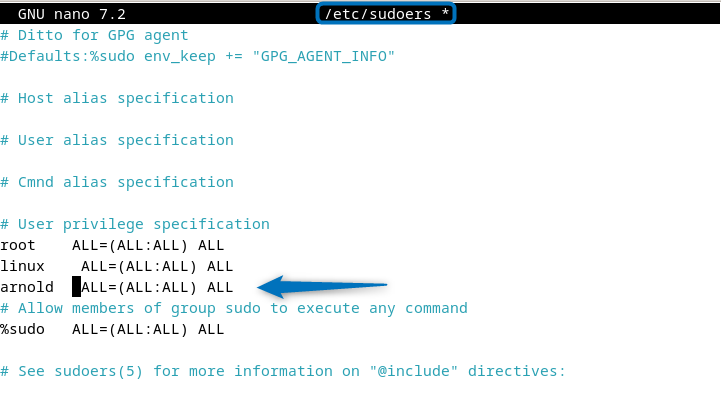
After adding the permissions for the respective user, save the sudoers file and then exit the root account. To verify, try executing the apt package update using the sudo command:
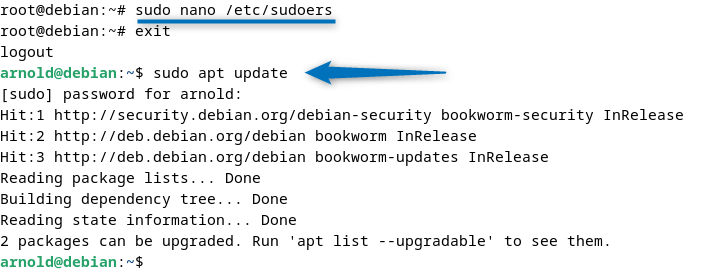
Furthermore, verify the permissions by listing information about the current user’s sudo permissions according to the sudoers file:
sudo -l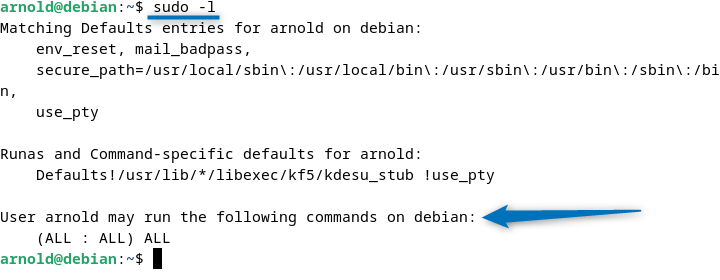
2: Through the usermod Command in Debian 12
Another way to add a user to sudoers in Debian is by using the usermod command, which is primarily used for editing any user data or permissions. On most Linux distributions, the sudo group is the one having admin privileges, so use the usermod command to add the respective user to the sudo group:
usermod -aG sudo [user-name]
To verify if the user is added to the sudoers file, list the users added to the sudo group:
groups [user-name]
3: Through the adduser Command in Debian 12
To add a user to any group or to create a new user in Debian, the adduser command is normally executed. A user in Debian can be added to the sudoers file by using the adduser command:
adduser [user-name] sudo
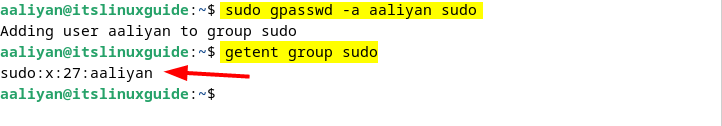
Further, to check if the user is added successfully, use the getent utility for listing users present in the sudo group:
getent group sudo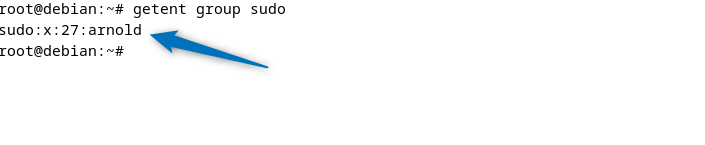
4: Through gpasswd Command
In Linux gpasswd command is primarily used for administering /etc/group and /etc/gshadow, meaning it manages group memberships and passwords so in case of Debian, use the following syntax to add a user to the sudo group:
sudo gpasswd -a [user-name] sudo
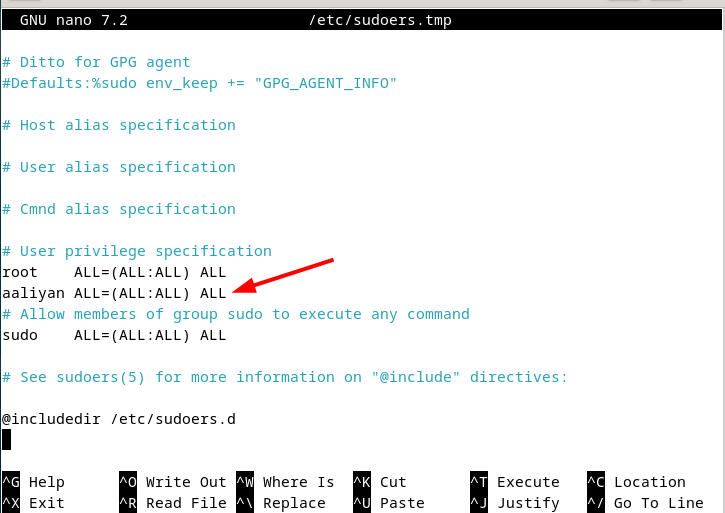
5: Through visudo Command
The visudo command primarily edits the sudoers file, as it directly opens the sudoers file without specifying its path in the command:
sudo visudo
Now paste the following code line with the desired username in the sudoers file:
[username] ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL
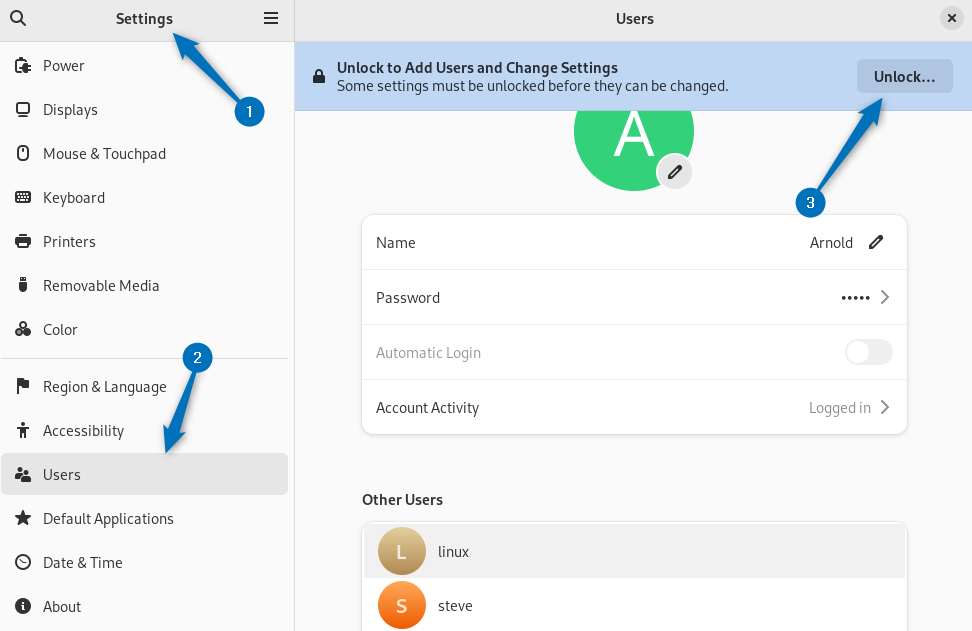
6: Through Debian User Settings
If using commands for adding a user in the sudoers file is not preferable, then do it through user settings. This method is recommended for users who are new to the Debian system and are not very familiar with command execution. Simply navigate to user settings and then unlock them by entering the authentication password:
Next, select the user that is to be added to the sudoers file and then turn on the administrator option:
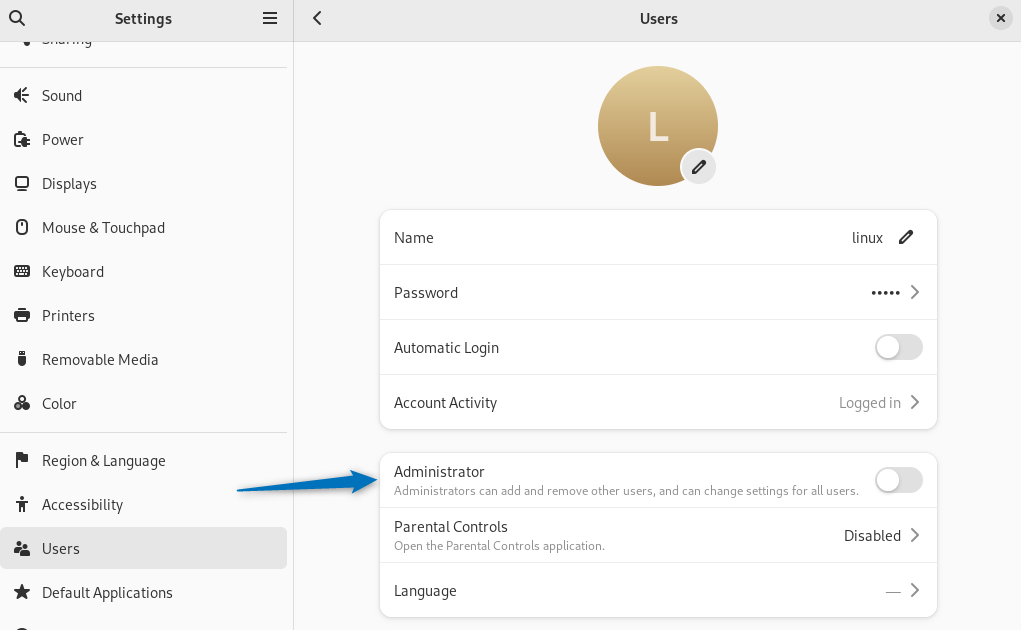
NOTE: Keep in mind that if there are multiple users on the system, then the user you want to add to the sudoers file must be logged out.
Conclusion
When a non-sudo user tries to execute a command using sudo the error of username is not in sudoers file appears. To add user to sudoers in Debian there are six ways, which include adding the permissions manually in the sudoers file, using the usermod command, using the adduser command, or using the system user settings. The easiest way to add user to the sudoers is by using the adduser command. Remember to switch to the root account before adding the user to the sudoers file.
