Apache Cassandra is a fault-tolerant, peer-to-peer, distributed NoSQL database optimized for petabyte-scale workloads, offering tunable consistency, high availability, and linear scalability across multi-data center deployments. To install Cassandra on Ubuntu, this guide will discuss four methods.
4 Ways to Install Cassandra on Ubuntu
To install Cassandra, there are four methods for Debian-based Linux systems; however, before going to the installation, it is necessary to have Java installed on the system. This is because Cassandra is entirely implemented on the JVM, and it relies on Java’s runtime features to deliver high performance, fault tolerance, and horizontal scalability in a distributed environment. So first check if Java is installed by executing the version command:
java -version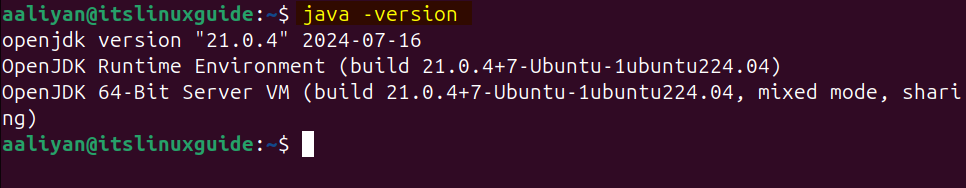
If Java is not installed, then use the following command:
sudo apt install default-jre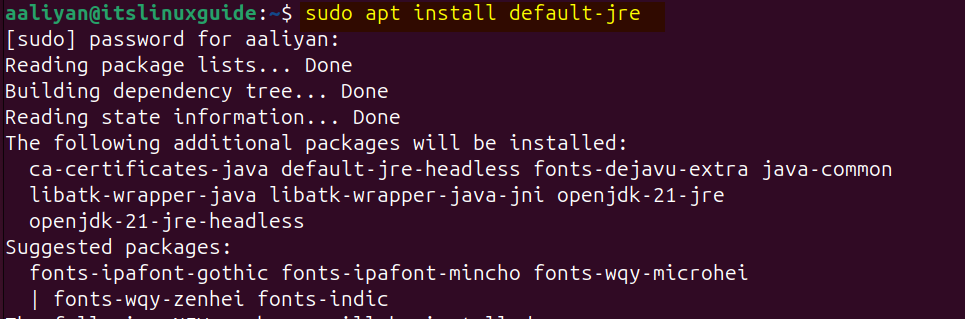
1: Through Cassandra Repository
The first method to install Cassandra on Ubuntu is to use its repository, as by default, the apt package installer does not have Cassandra, so execute the following command:
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/apache-cassandra.asc] https://debian.cassandra.apache.org 41x main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cassandra.sources.list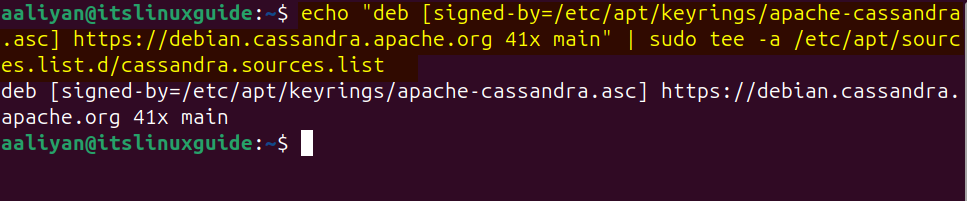
Next, download and add the .asc file for Cassandra by executing:
sudo curl -o /etc/apt/keyrings/apache-cassandra.asc https://downloads.apache.org/cassandra/KEYS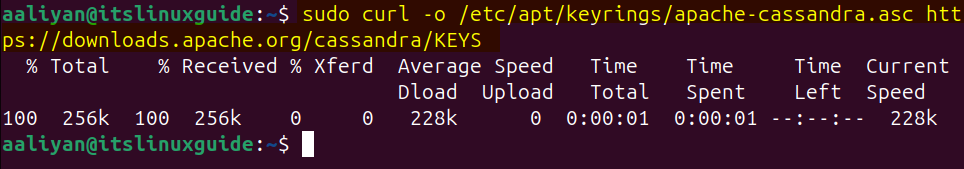
Now, update the apt repository to add the Cassandra repository successfully:
sudo apt-get update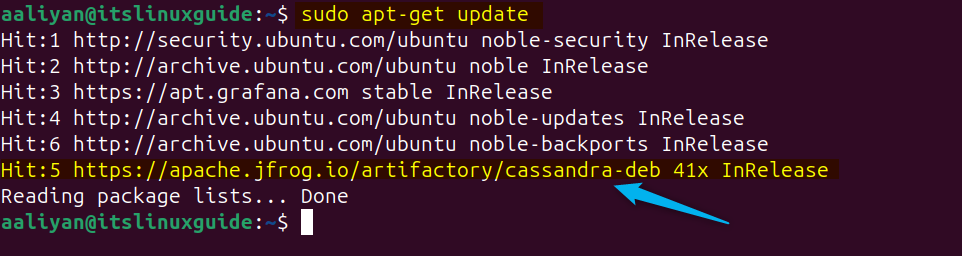
Install Cassandra on Ubuntu using its default package installer:
sudo apt install cassandra -y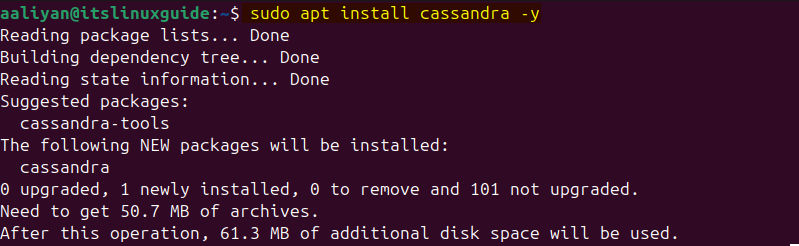
To verify the Cassandra installation, check its service status by executing:
sudo systemctl status cassandra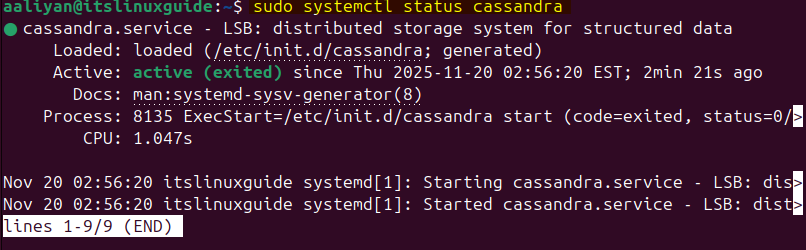
2: Through Docker Image
Another method to install Cassandra is via the Docker image. This is useful as Docker provides an isolated, reproducible, and easily deployable environment that avoids system-level conflicts, simplifies cluster creation, and accelerates development workflows. To install Cassandra via Docker on Ubuntu, execute:
sudo docker pull cassandra:latest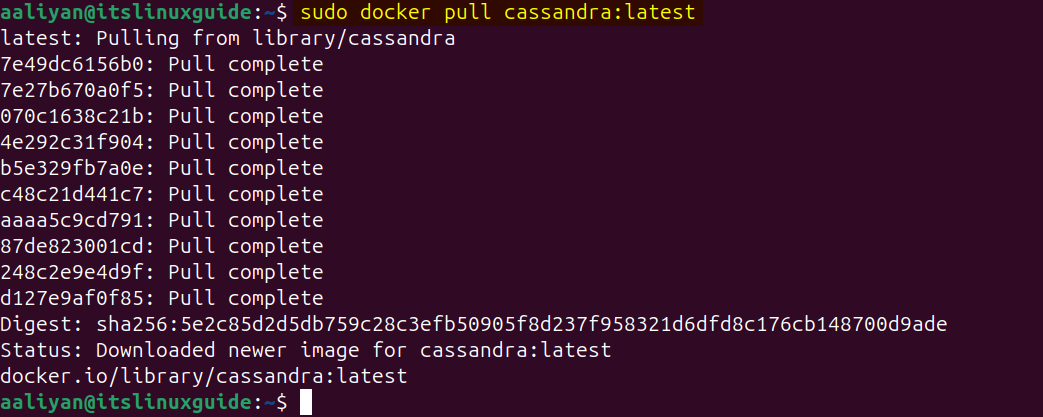
Furthermore, list all the Docker images to verify the installation of Cassandra:
sudo docker images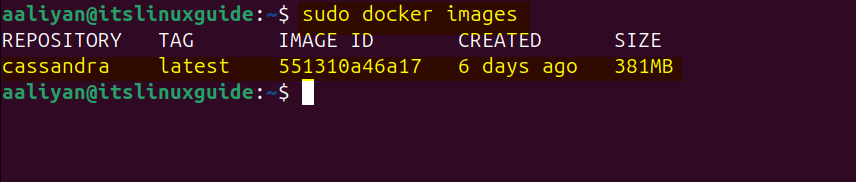
3: Through Cassandra Tar File
Cassandra, via its source file, comes with a plug-and-play version, which is primarily used by developers as the build file can be customised as per required specifications. Download the source file either manually or use the following command:
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/cassandra/5.0.6/apache-cassandra-5.0.6-src.tar.gz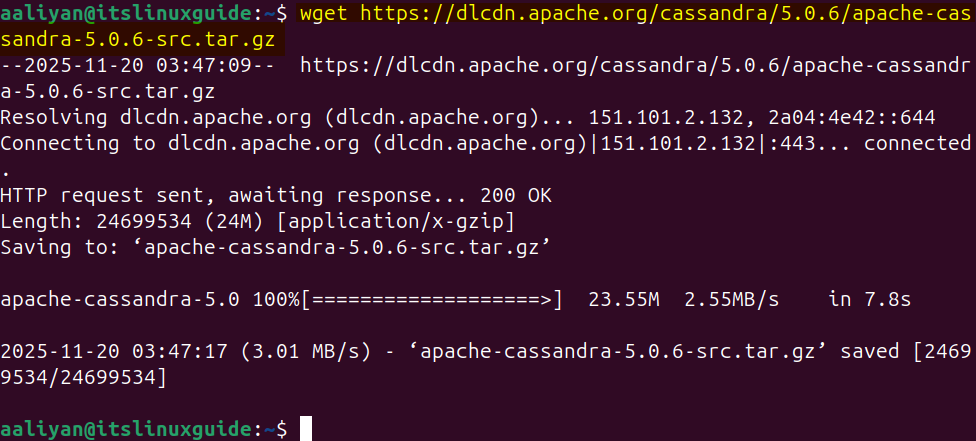
Next, extract the Cassandra tar file using the Tar utility by executing:
tar xzvf apache-cassandra-5.0.6-src.tar.gz
In Cassandra, a cluster is a collection of nodes that operate together as a single distributed database, where data is automatically partitioned, replicated, and managed across all nodes. So open the .yaml file in the conf directory and rename the cluster to a desired name:
sudo nano cassandra.yaml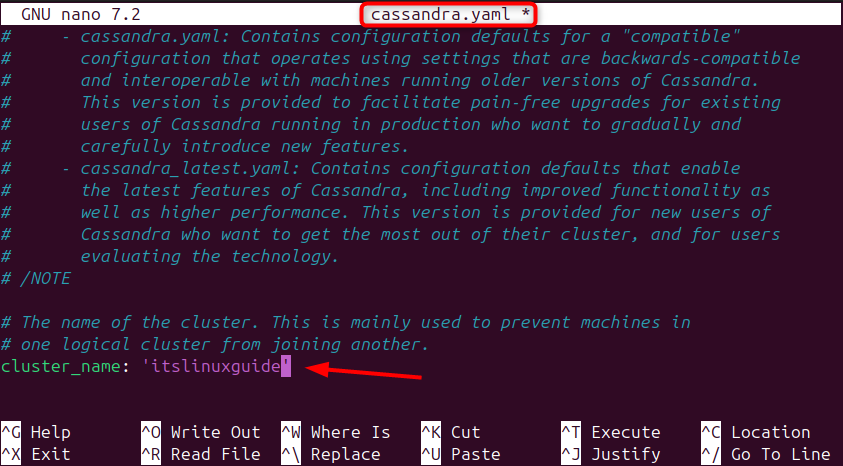
Next, execute the Cassandra script in the bin directory of the extracted file using the following command:
bin/cassandra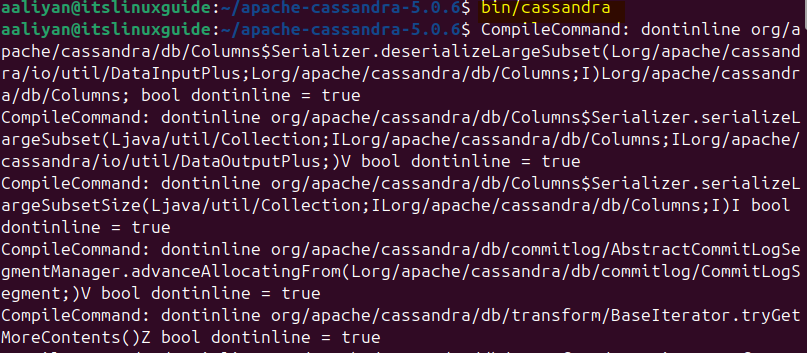
In case there is any sort of error while execution, build the source file by executing the following command:
ant -Dant.gen-doc.skip=trueFurthermore, running Cassandra after building the source file may require Python version 3.6-3.11 and Java version 17, as it does not support Java 21. Execute the following command to query the Cassandra cluster via JMX and display the real-time operational state, health, and data distribution of all nodes in the cluster:
bin/nodetool status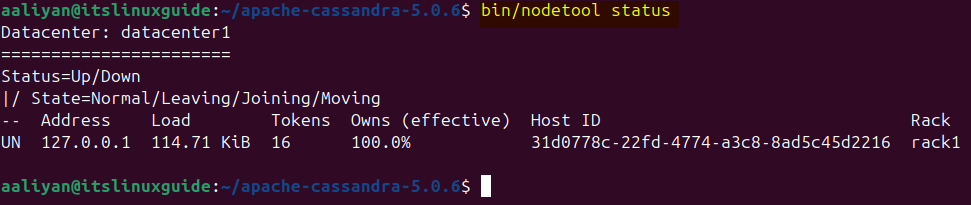
4: Through Snap Package Installer
Snap is an isolated, self-contained, and cross-distribution format that runs consistently across different Linux environments. To install Cassandra on Ubuntu, execute the following command:
sudo snap install charmed-cassandra --edge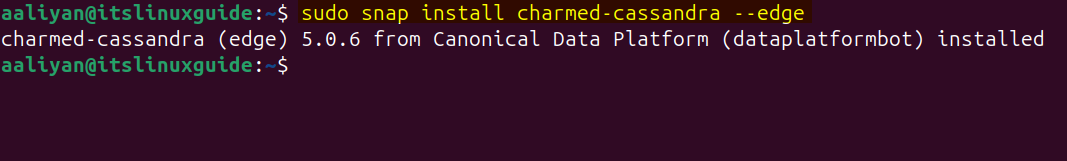
Verify Cassandra installation via snap by listing all of its installed apps using the following command:
sudo snap list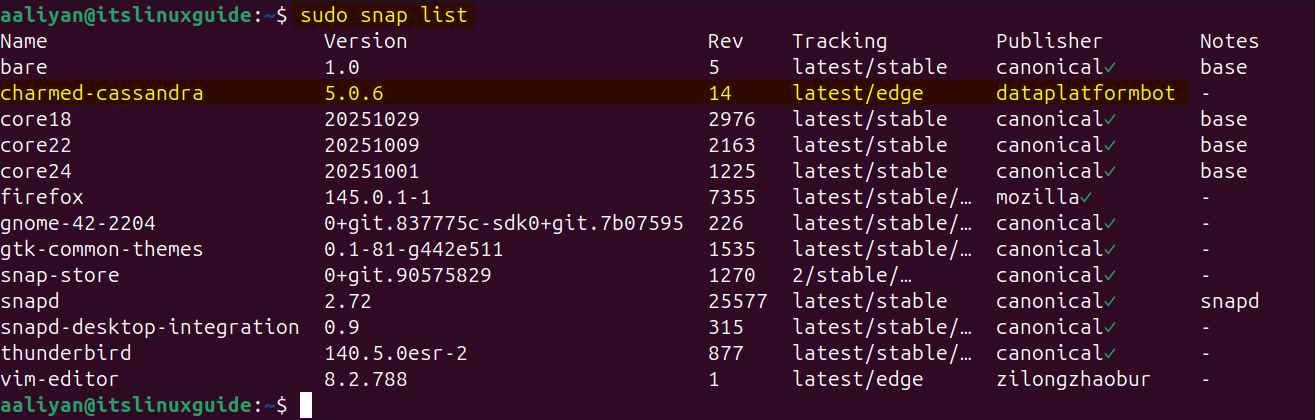
Conclusion
Ubuntu is an ideal platform for Cassandra because it provides a stable, secure, high-performance, and dependency-friendly environment. To install Cassandra on Ubuntu, the four methods are available: using the Cassandra repository, source file, Docker image and Snap package installer.
