Linux distributions like Debian 12 originally were only limited to the command line interface and their use was only limited to those who have sound knowledge about command execution. With the introduction of different desktop environments for Linux distributions there is a drastic increase in its users.
Since most people use Windows and MacOS, the Linux-based desktop environment interface can be transformed like Windows and Mac on Linux. The lightweight design and extensive customization options of Xfce make it one of the most popular desktop environments. We will explore all the possible ways to install Xfce on Debian 12 in this blog post.
How to Install Xfce on Debian 12
Xfce strikes a balance between resource efficiency, customization, and a familiar interface, making it a popular choice for Debian and other Linux distribution users. To install it on Debian 12 there are three ways which can be used:
1: Through Debian 12 Default Package Installer
One of the easiest and fastest-track methods to install Xfce on Debian 12 is using its advanced packaging tool (apt) which is its default package installer. To install Xfce of Debian use:
sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies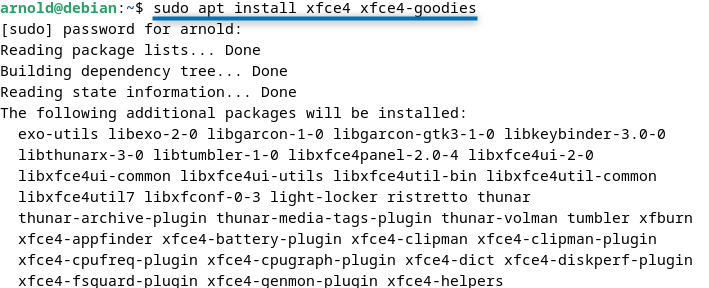
During the installation, a package configuration tab will open asking for configuring the display manager for Xfce. Display managers act as a bridge between users and the display server (such as X Window System or Wayland).
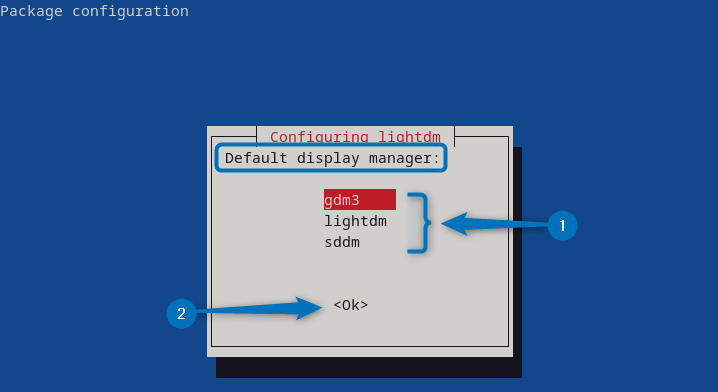
The configuration will ask about selecting the display manager and will show three options which include gdm3, lightdm, and sddm. The best option among all is sddm as it is compatible with Debian and also unlike lightdm it shows all the other users as well on the login page. So select the desired display manager and then click on OK to proceed:
Once the process is completed reboot the system using:
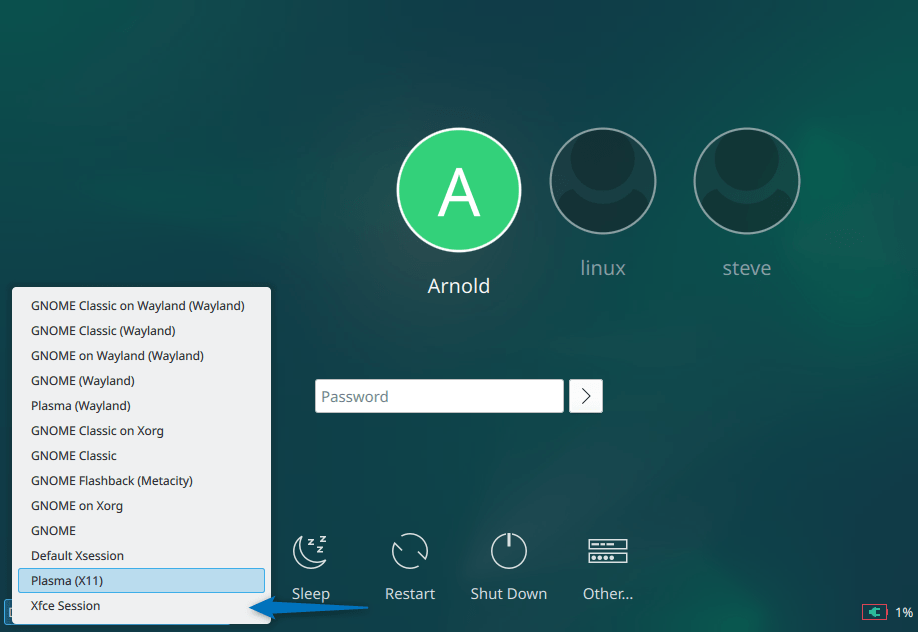
sudo rebootNow on the login page select the Xfce session option and then log in as the desired user:
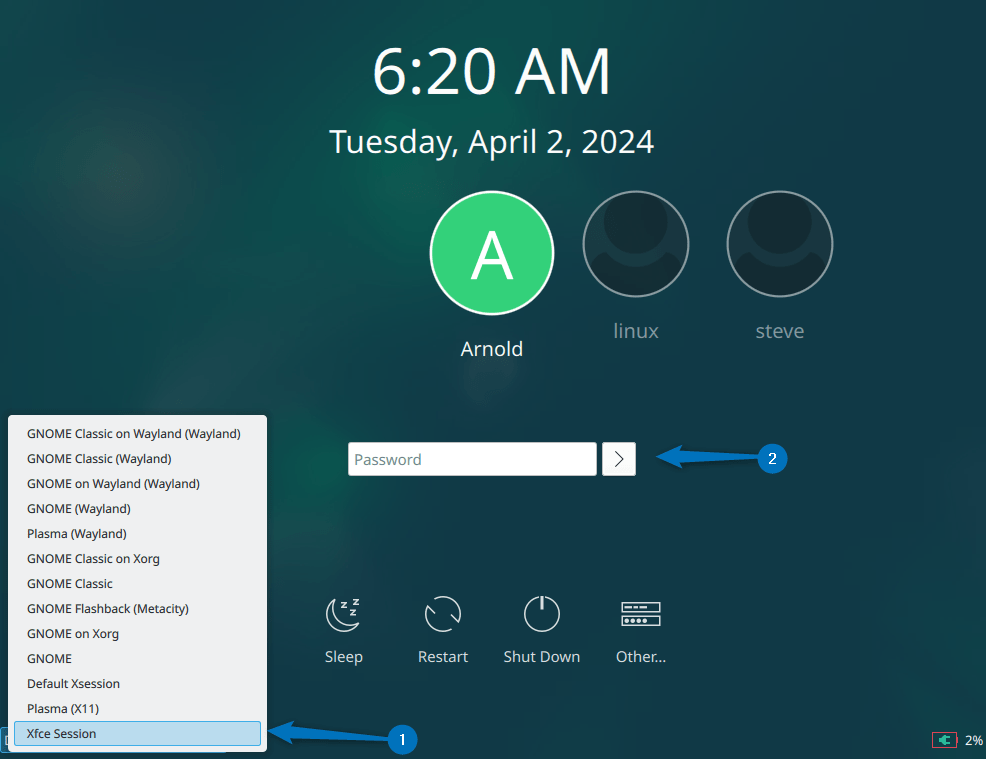
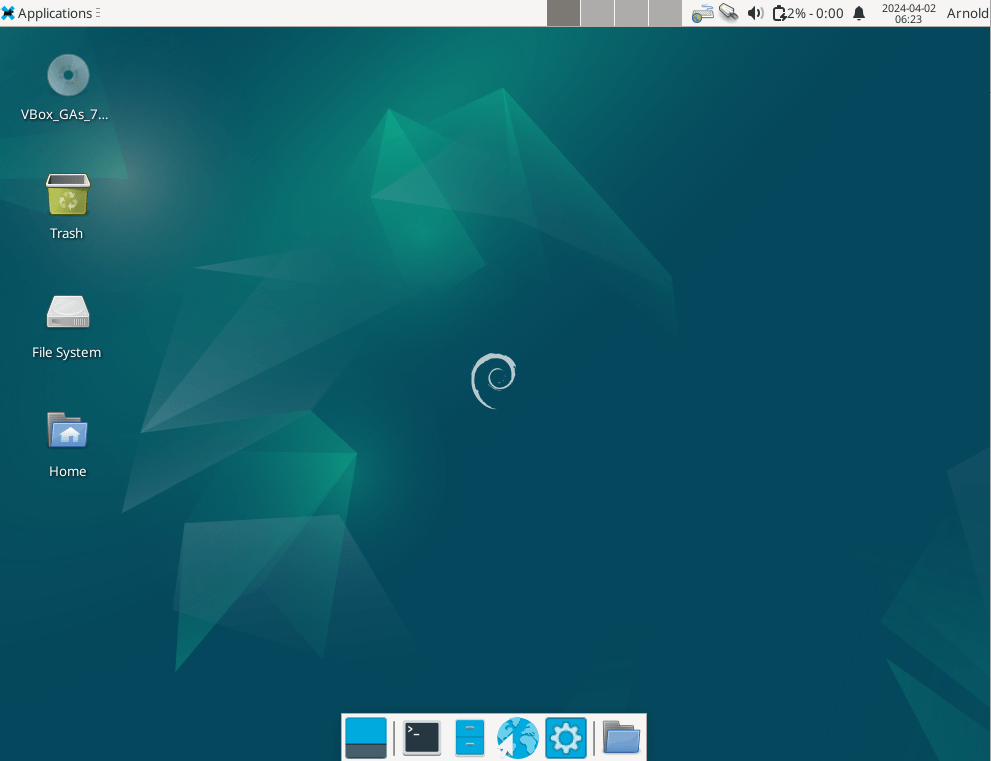
The interface of the Xfce session will look like this as in the image below:
Now you can further verify the desktop environment by using the screenfetch utility tool:
screenfetch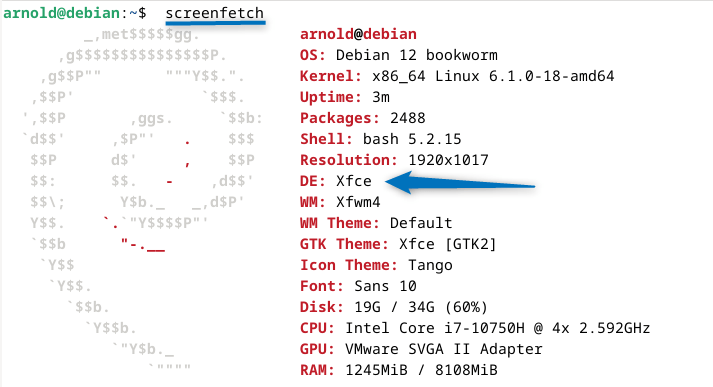
2: Through tasksel Uility
Another way to install Xfce on Debian 12 is by using the tasksel utility. Tasksel is a Debian/Ubuntu tool that simplifies the installation of multiple related packages by grouping them into coordinated “tasks. To install Xfce via taksel use:
sudo tasksel install xfce-desktopThe process for installation will began:
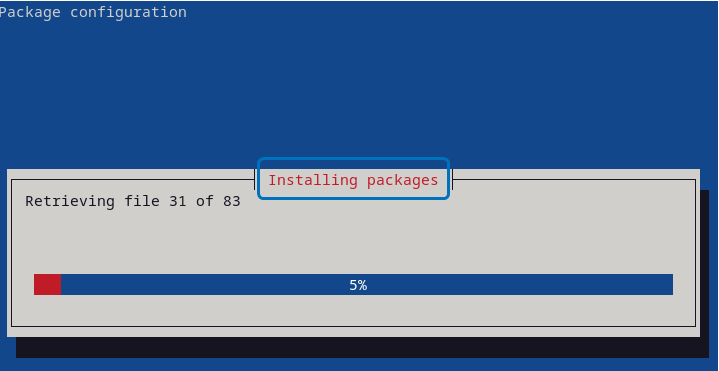
It might ask you to install a display manager if you were previously using Debian default display manager. Here I already had sddm installed so the installation window closes once the installation is completed. Reboot the Debian and select the Xfce desktop environment from the login page:
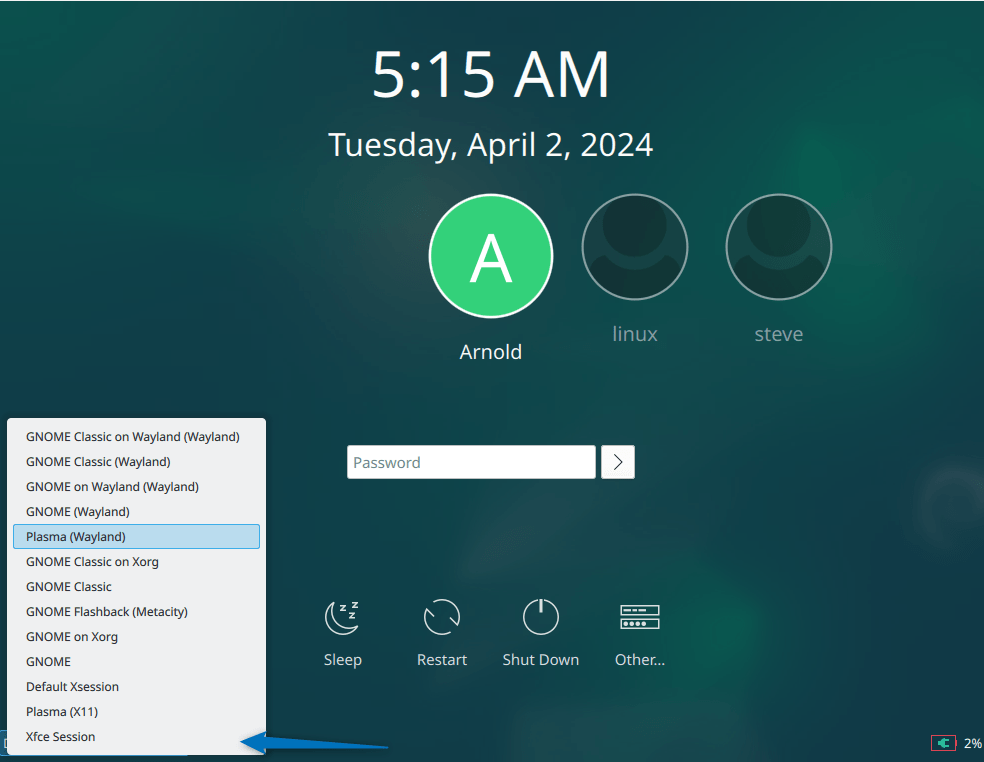
The interface of the Xfce session will look like this as in the image below:
Furthermore, you can also verify the installation of Xfce on Debian 12 by executing the list command for tasksel utility:
tasksel --list-tasks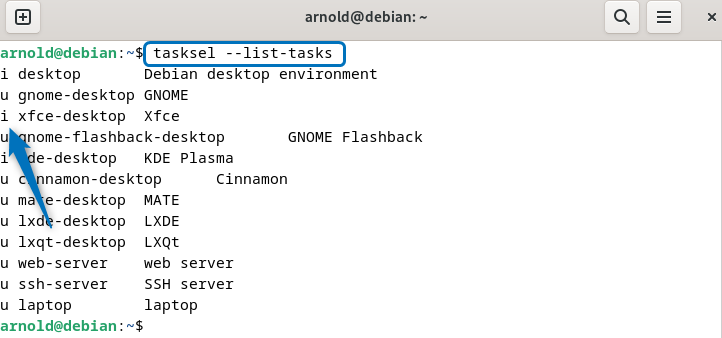
Here, you can see i flag with xfce-desktop which means it is installed on Debian 12.
3: Through Synaptic Package Manager
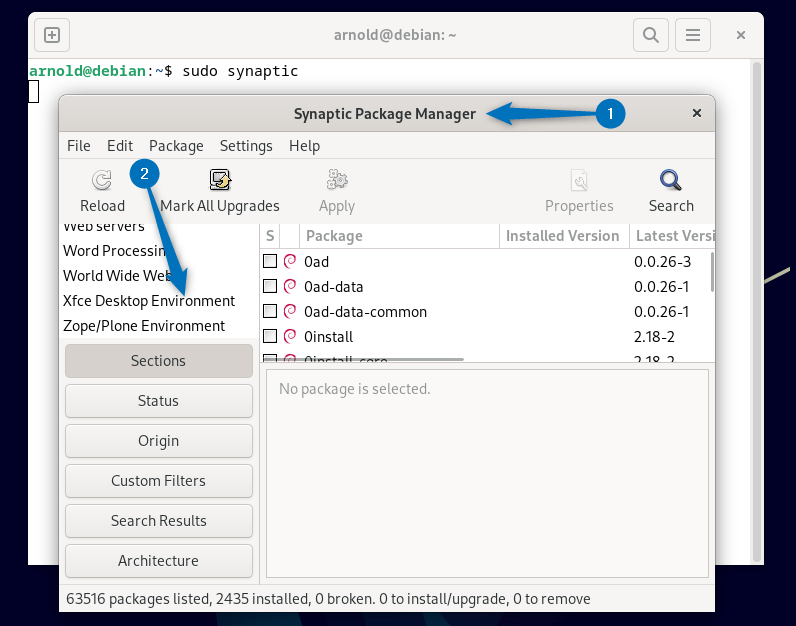
Synaptic Package Manager is a lightweight GUI front end to the apt package management system. It is widely used in Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and other Debian/Ubuntu-based distributions. To install Xfce on Debian first either launch it via the applications menu or use:
sudo synapticNow at the end of the list of programs you will find Xfce Desktop Environment:
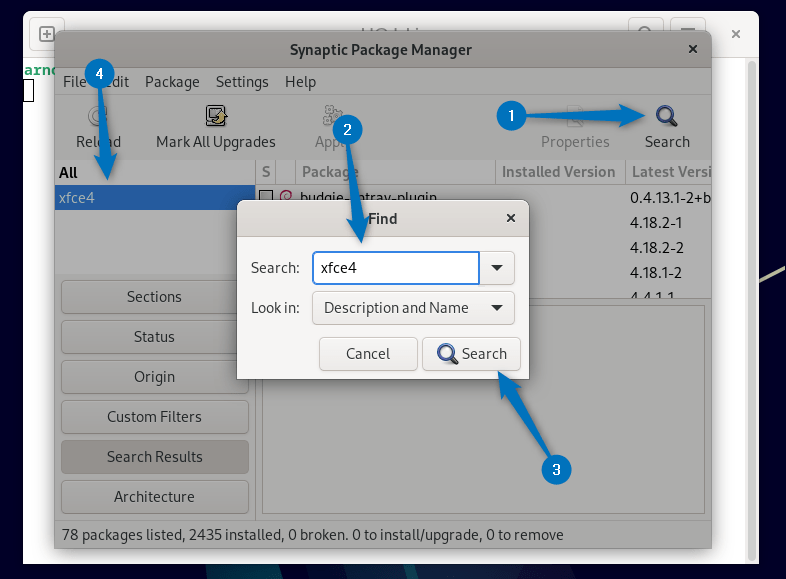
Here once you select the Xfce Desktop Environment all the related packages will be selected but you have to manually select other plugins to install it successfully. Alternatively, you can also find the Xfce by searching it:
Now the default packages are automatically selected but to have full experience of the Xfce desktop environment you have to select other packages manually like the plugin for app finder, date/time, and more:
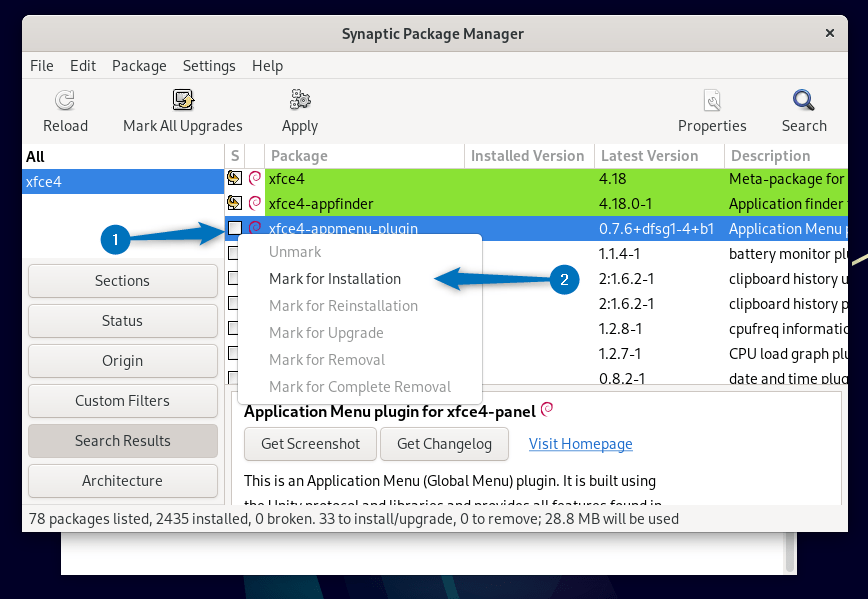
Here now I have manually added the below selected plugins for Xfce:
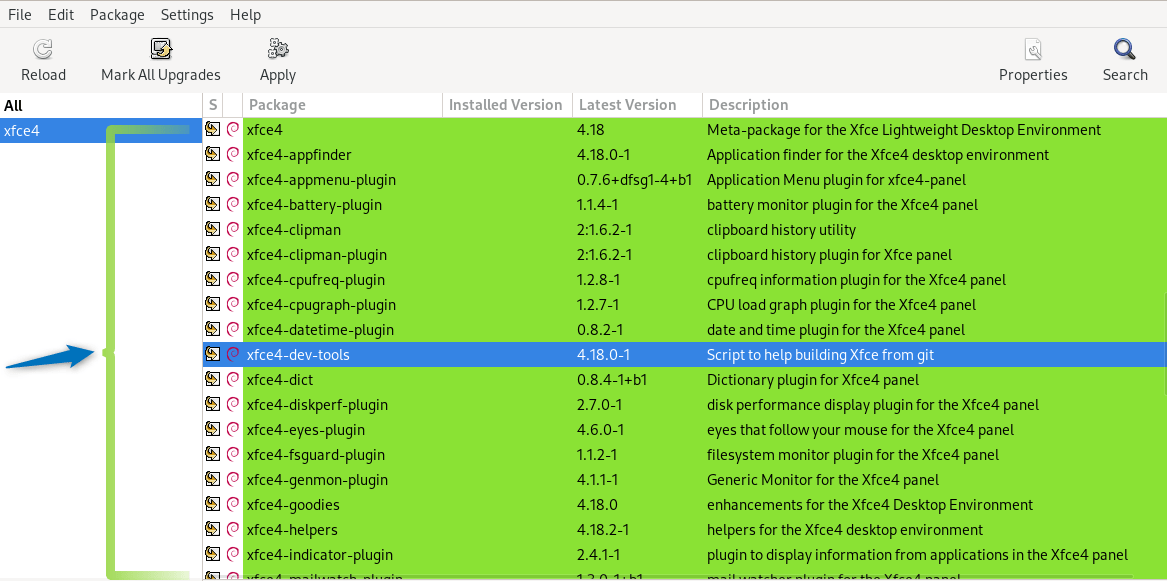
Here are some other packages that I have installed for Xfce without them you won’t be able to install it:
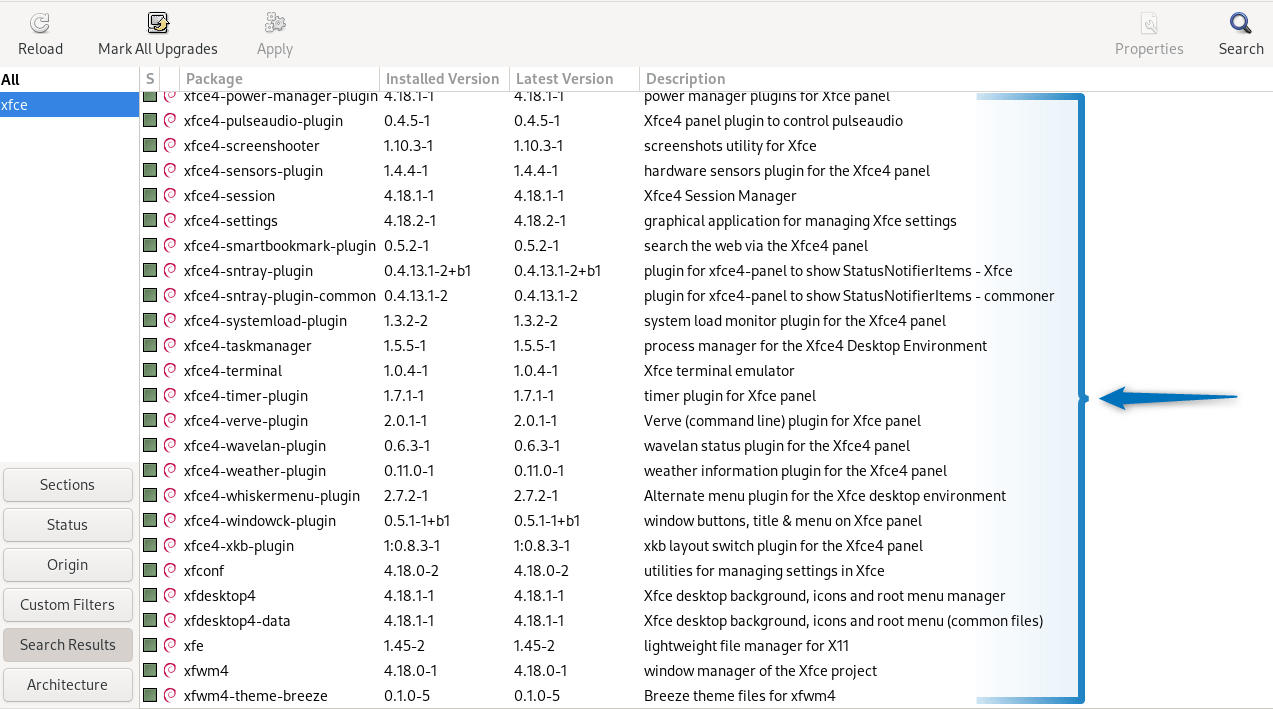
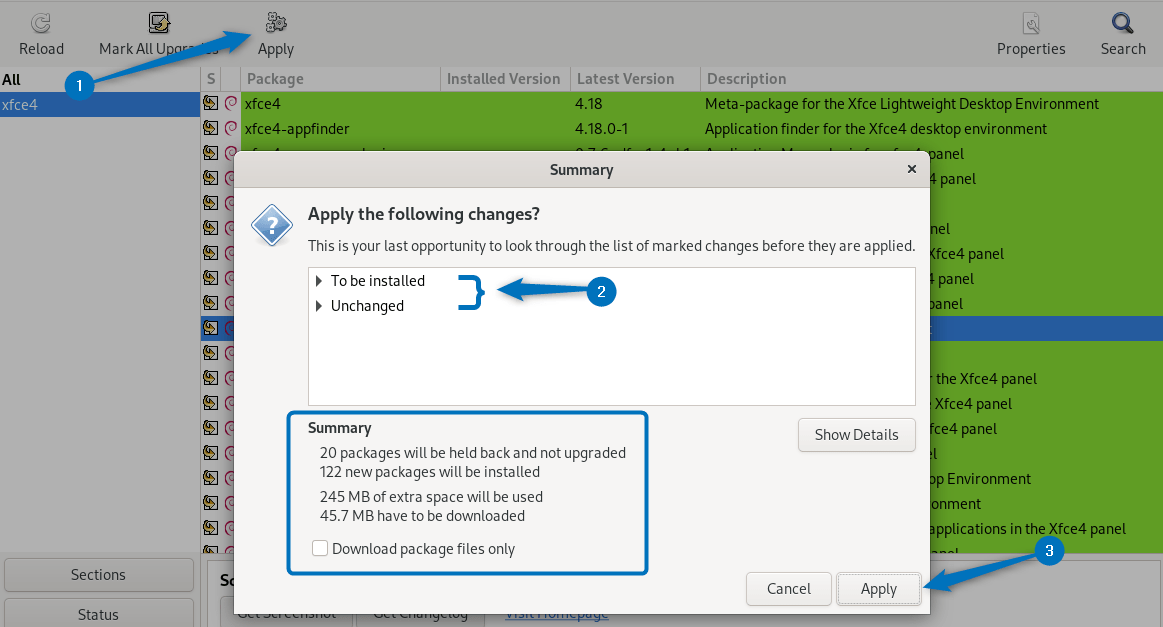
Now to install Xfce on Debian 12 click on the Apply option and prompt the installation by clicking on the Apply option. Further, you can verify the packages that are to be installed by opening up the tray for To be installed:
Once the installation is started the installer will ask about installing the display manager and here I have selected sddm:
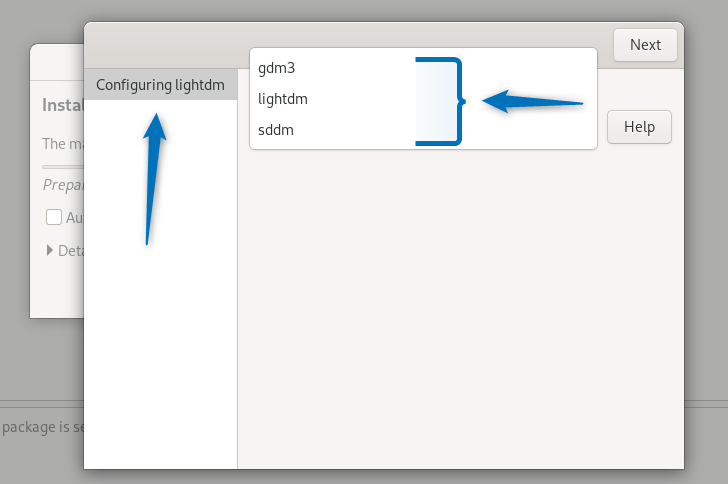
Now once you are done with the display manager selection click on next to proceed:
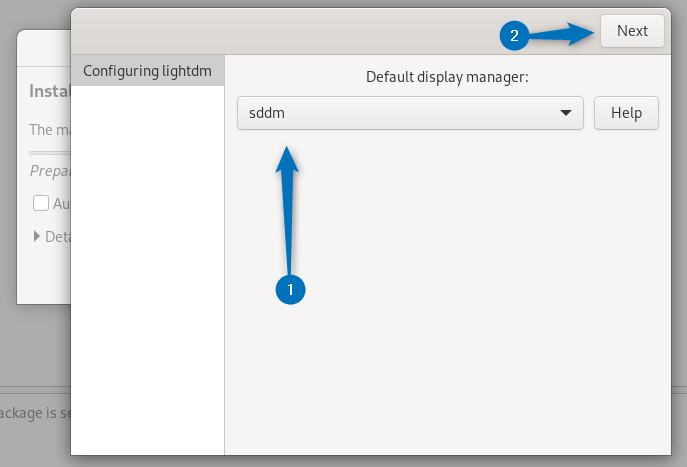
Now the installation will begin:
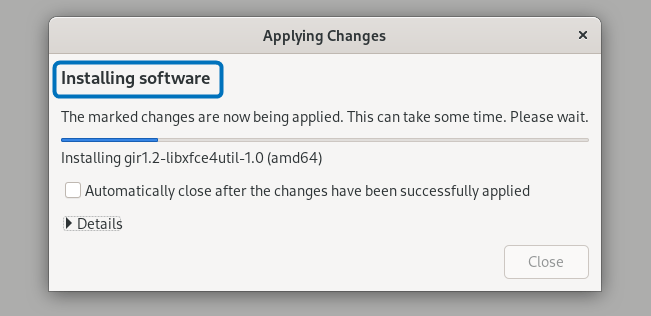
After the process is completed close the installation window:
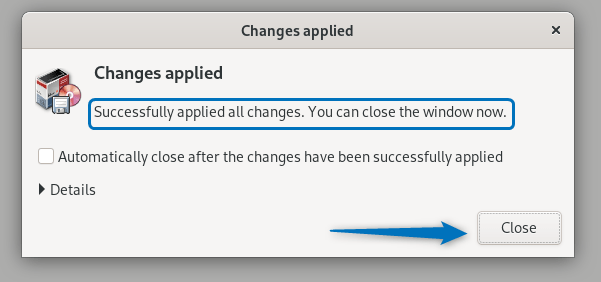
Now reboot your system and change your Debian desktop environment from GNOME to Xfce session:
Synaptic is usually pre-installed on Debian 12 but in case if it is not pre-installed then use:
sudo apt install synapticConclusion
Xfce on Debian 12 can be installed by using three methods which include using its default app installer, taskel utility, and synaptic package manager. For Debian 12 to switch between different desktop environments I think that sddm is the best display manager as it is compatible not only with KDE but also with other desktop environments. Furthermore, it is lightweight and because of that, it uses quite less system resources.
