Redis is a remote dictionary server that uses the in-memory storage system which, unlike traditional relational databases, uses RAM for data retrieval and storage. You should install it if you need fast data access, multiple data structures, and real-time messaging on Debian. Redis comes with two licenses one is Source Available License v2 and the other is Server Side Public License v1, if you are a beginner then start with the free version which is the Source Available License. To install Redis on Debian, read this guide as it will explain multiple ways of installation.
4 Ways To Install Redis on Debian
Redis is used in high-traffic websites, e-commerce platforms, real-time chat, and social media applications. Further, it is also used by mobile app and web developers, to install Redis on Debian, there are primarily four ways which this guide will discuss:
1: Through Redis Official Repository
The first method to install Redis on Debian is using Redis official repository, this method is suitable if you are looking for the latest version of Redis. To install Redis on Debian via its repository, add its GPG key first for package validation:
curl -fsSL https://packages.redis.io/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg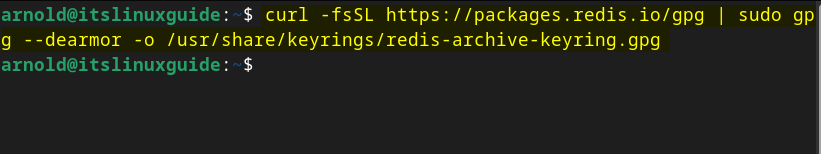
Next, add the Redis repository on Debian in its sources directory signed by the GPG key added previously:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/redis-archive-keyring.gpg] https://packages.redis.io/deb $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/redis.list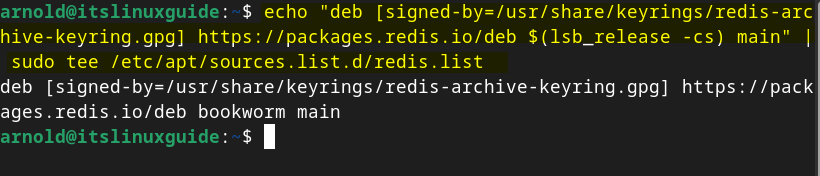
Now update the apt packages list so that Redis repository is added successfully:
sudo apt-get update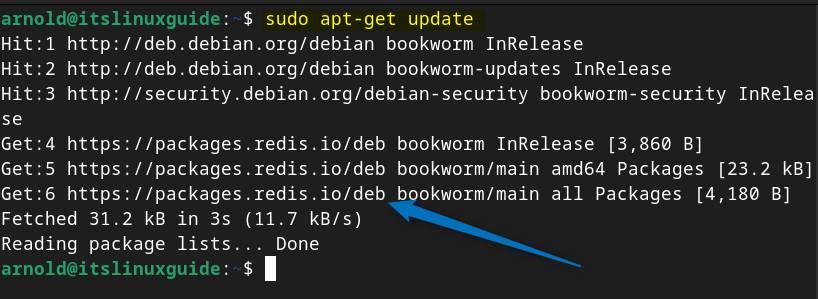
Now use the apt package manager to install Redis on Debian by running the following g command:
sudo apt-get install redis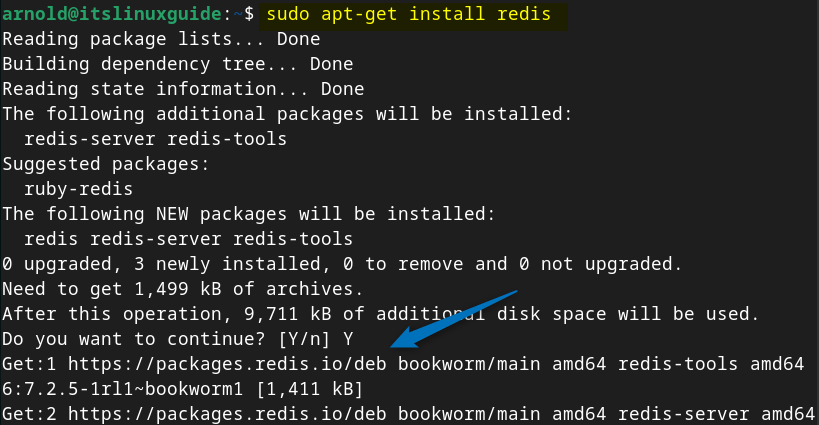
Before launching or using Redis on Debian you need to do some configurations which will be discussed in the later section. Since the apt package manager installs the command line version, so execute the below command to launch Redis on Debian:
redis-cli
2: Through Snap App Installer
The next method to install Redis on Debian is using a third-party package installer named Snap, to install Redis via Snap execute the below command:
sudo snap install redis
Now to confirm the Redis installation on Debian via Snap list all the Snap-installed apps:
sudo snap list
To launch Redis on Debian installed via Snap you need to start the Redis service, so to start the Redis service execute:
sudo snap start redis
Next, verify if the Redis service is active or not by executing the below command:
sudo snap services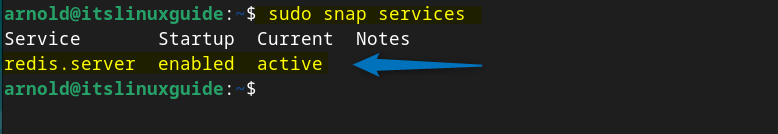
Now launch Redis on Debian by using the snap run command:
sudo snap run redis.cli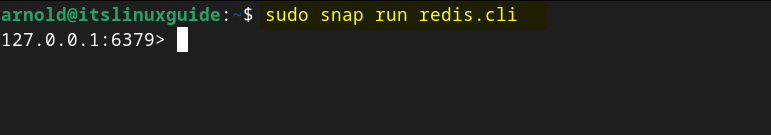
Redis also comes with a sort of GUI version named RedisInsight, it allows users to optimize and visualize their databases with the help of its user-friendly interface. So if you are more inclined towards using Redis GUI version then execute the below command:
sudo snap install redisinsight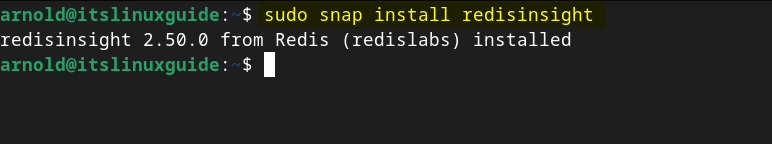
Further to launch Redis GUI installed via Snap execute the below command:
redisinsight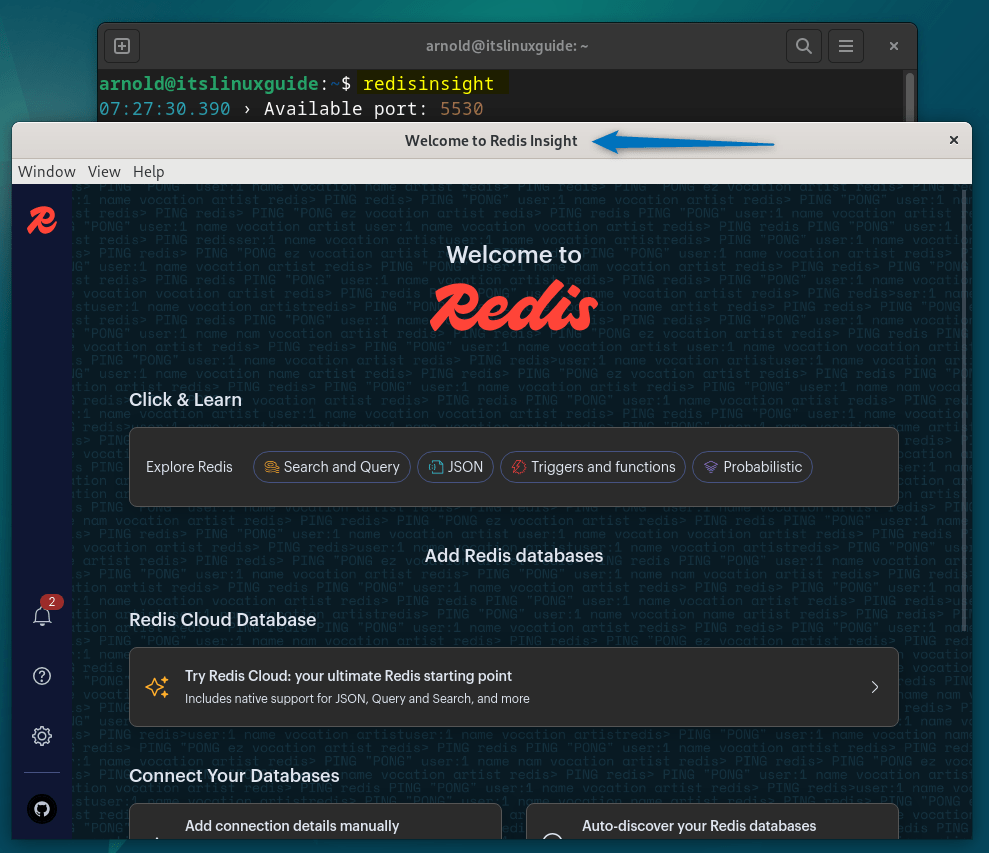
3: Through Flatpak App Installer
Another way to install Redis GUI version on Debian is by using the Flathub repository which is used by the Fatpak app installer. To install RedisInsight on Debian via Flatpak execute:
flatpak install flathub com.redis.RedisInsight
For RedisInsight you do not need to do any configurations from the command line as you can set everything from within the application to launch it execute:
flatpak run com.redis.RedisInsight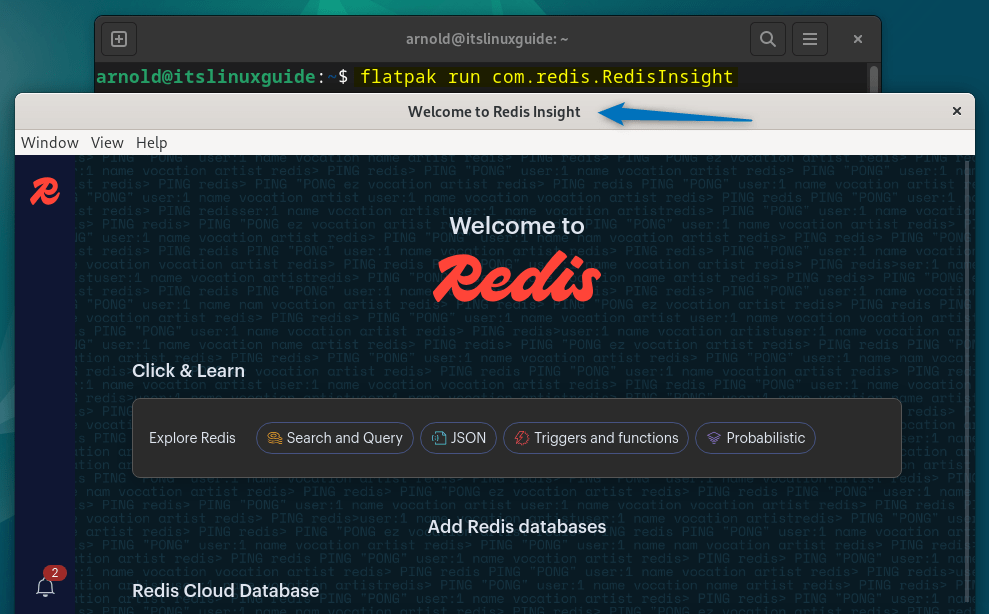
4: Through Debian Default Repository
The default Debian package manager comes with Redis server repository but the version will be older. However, to install Redis via apt package manager execute:
sudo apt install redis-server
After carrying out the necessary configuration steps for Redis execute the below command to launch it:
redis-cli
How To Configure Redis On Debian 12
The first thing you need to do after installing Redis on Debian, either via its official repository or the Debian default repository, is to change the supervised setting to systemd in its configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/redis/redis.confThis is because Debian uses the systemd init system so changing it to systemd will declare the init system for managing Redis as a service, thus allowing the user more control:
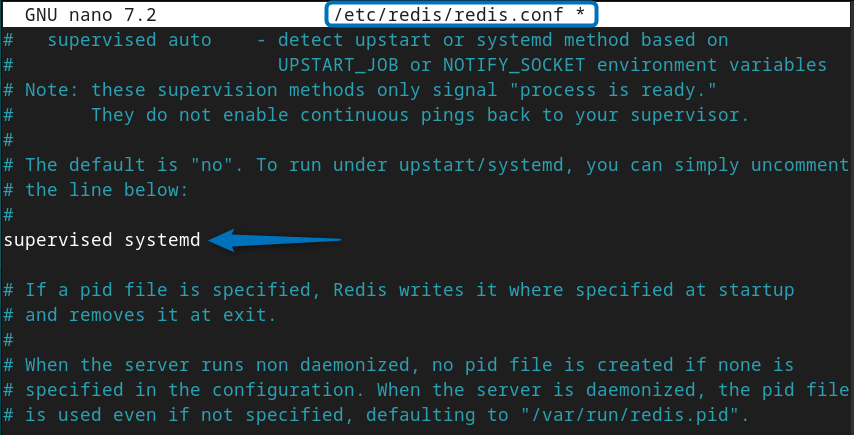
Once you are done with the changes then save the file and close it, after that reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes by executing:
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadAnother thing that you need to remember is whether you are using the apt package manager or Redis repository to install Redis do not use the below command as some blogs have mentioned it:
sudo systemctl status redis
To check the status of the Redis service on Debian use the following command:
sudo systemctl status redis-serverHere in the below image, you can see that Redis service is active but not enabled:
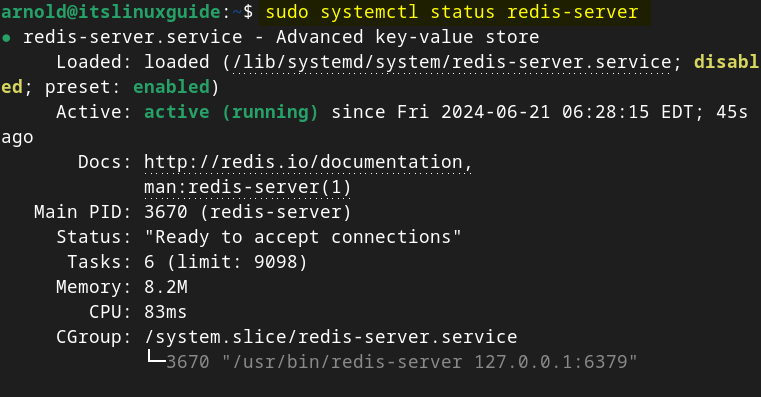
So to enable the Redis service on Debian execute:
sudo systemctl enable redis-server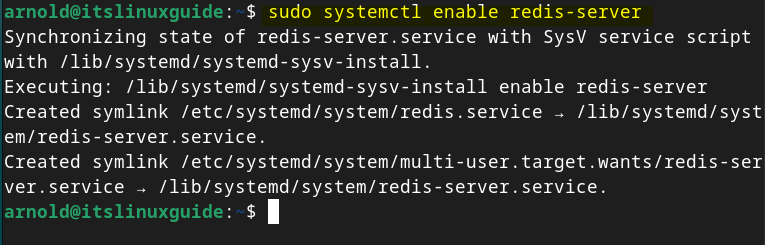
Note: I have also tried installing Redis using its source file on Debian but while installing the make file I encountered various unsolvable errors so try avoiding that method.
Redis comes with different versions and these include Redis Enterprise software,Redis Community Edition & Stack, and Redis Insight so here in the table below I have compared all these, which will help you in choosing which one is best for you:
| Features | Redis Community Edition (Open Source) | Redis Stack | Redis Enterprise Software |
| Basic caching | Available | Available | Available |
| Support options | Limited | Varies | Enterprise-grade support |
| Object mapping libraries | Available | Available | Available |
| Advanced features | Not Available | Available (Querying, indexing, etc.) | Available (Geo-distributed Redis) |
| Disaster recovery | Not Available | Not Available | Available |
| Automated deployment | Not Available | Not Available | Available ((On-premise, cloud, K8s) |
| In-memory capacity extension | Not Available | Not Available | Available (SSD) |
| High availability | Not Available | Not Available | Available |
| Data models | Flexible | Flexible | JSON Support |
| Scalability | Smaller-scale | Extends Redis capabilities | Enterprise-scale operations |
| Cost | Free | Varies (based on features) | Contact Redis Labs for pricing |
Conclusion
To install Redis on Debian there are primarily four ways, these include using Redis’s official repository, the Snap app installer, Flatpak package manager, and using Debian default repository (apt). If you are more interested in the Redis GUI version then either use Snap or Flatpak, otherwise use the Redis official repository method.
